CSAPP CacheLab (CMU)
实验环境:Ubuntu 18.04,ThinkStation P500
Cache Lab 简介
-
实验共有两个部分,Part A 和 Part B,主要目的是为加深对 CPU Cache Memory 的理解。
-
Part A要求使用C language实现一个Cache模拟器,主要要求了解Cache的寻址方式,以及 LRU(Least Recently Used) 算法的工作方式,测试是以动态分析工具 valgrind 为基础,对照标准程序的 Miss,Hit,Evict 给分。
-
Part B要求实现一个矩阵转置的函数,用以测试 32x32,64x64,61x67的矩阵样例,要求Cache在满足参数 (1024B,s=5,E=1,b=5) 的条件下,Miss满足测试标准。
(细节参考Cachelab Description.pdf )
Part A
问题分析
- Cache模拟的实现的问题主要集中在两个方面:
- Cache的数据结构(如果采用抽象的数据结构可以略过这个点)
- Cache的寻址方式
这两个问题都可以由 CSAPP 6.4.3 来解答,即组关联 Cache 的结构
CASPP插图
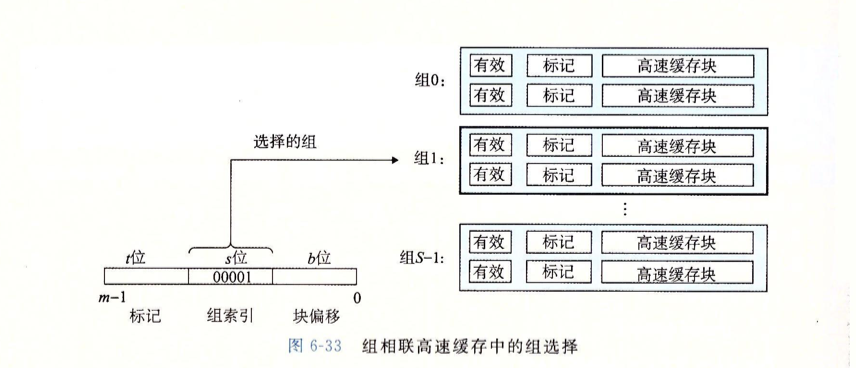
- 由这张图可以得到以下几点:
- 左下角为地址格式 (在实验中即64位),中间的s位组索引及我们的 Terminal参数”-s”,其用来索引组号,因此共用 $S=2^s$ 组。
- 在用组索引确定了具体组之后,用地址中的前t位(具体位数由公式 $t=m-s-b$ 间接计算) 与Cache 中的标记位做比对,如果存在 (有匹配成功的行) 则 Hit,反之 Miss,根据指令类型与Cache是否满确定是否有进一步操作(如 Evict)。
- 地址的最后b位 (即 Termial 参数”-b”) 块偏移表示块的大小,其用于索引目标块(行)中的缓存,共可以索引 $B=2^b$ 位。
- $t=m-s-b$ 中的 $m$ 即指令的位数。
具体实现
- 我们用一个 Struct 嵌套的层级结构来表示 Cache
| struct cache
├── struct cacheSet
├── struct setLine
├── int valid
├── int tag
├── char* block
└── (help) int timeStamp
timeStamp 用来确定在 LRU 下要 Evict 的缓存
具体代码实现如下:
typedef struct{
// Three fundamental parameters in perline
int valid;
unsigned long long tag;
char *block;
// choose which to evict in LRU
int timeStamp;
} setLine;
//set struct
typedef struct{
setLine *lines;
} cacheSet;
//cache struct
typedef struct{
cacheSet *sets;
} cache;
- 用一个结构体 cachePara 来储存 Cache 参数及最终结果(Miss, Hit, Evict)
typedef struct{
int s;//Number of set index bits (S = 2^s is the number of sets)
int S;//S=2^s
int b;//Number of block bits (B = 2^b is the block size)
int B;//B=2^b
int E;//Associativity (number of lines per set)
int verbosity;//Optional verbose flag that displays trace info
//LRU output
int hitNum;
int missNum;
int evictionNum;
} cachePara;
- 主函数 main() 主要负责以下两个个部分:
- 利用”getopt.h”从 terminal 读取参数初始化结构体 CachePara
- 从trace文件读取指令, 同时调取函数Simulate进行模拟
int main(int argc, char** argv){
//init cache structure
cache LRUcache;
cachePara parameters;
parameters.verbosity=0;
//use getopt.h to read data from terminal, store them in parameters(1)
char input;
char *trace;
while( (input=getopt(argc,argv,"s:E:b:t:vh")) != -1){
switch(input){
case 's':
parameters.s = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'E':
parameters.E = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
parameters.b = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 't':
trace = optarg;
break;
case 'v':
parameters.verbosity = 1;
break;
// print parameter prototype
case 'h':
printUsage();
exit(0);
default:
printUsage();
exit(-1);
}
}
//init parameters(2)
parameters.S = pow(2.0,parameters.s);
parameters.B = pow(2.0,parameters.b);
parameters.missNum = 0;
parameters.hitNum = 0;
parameters.evictionNum = 0;
//cache init
LRUcache = initCache(parameters);
//imput trace file while simulation
char command;
int size;
unsigned long long address;
FILE *file;
file=fopen(trace,"r");
while(fscanf(file," %c %llx,%d",&command,&address,&size)==3){
switch(command){
case 'I':
break;
case 'L': //Load
parameters = simulate(LRUcache, parameters, address);
break;
case 'S': //Store
parameters = simulate(LRUcache, parameters, address);
break;
case 'M': //Modify
parameters = simulate(LRUcache, parameters, address);
parameters = simulate(LRUcache, parameters, address);
break;
default: //ignore 'I'
break;
}
}
printSummary(parameters.hitNum,parameters.missNum,parameters.evictionNum);
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
- 我们区别I、M、S指令的问题放在Main()的层级上解决,即Simulate()函数只负责访问Cache内的目标内容,若存在则Hit;若不存在,则 Evict (若CacheSet已满) 再 Load 进入 Cache。之后 Simulate() 将结果储存在 CachePara 内。
Simulate()函数如下:
cachePara simulate(cache currentCache, cachePara parameters, unsigned long long address){
//get the tag
int tagSize = 64-(parameters.b + parameters.s); //64 bit system
unsigned long long tag = address >> (parameters.s + parameters.b);
//get the set index
unsigned long long tmp = address << (tagSize);
unsigned long long setIndex = tmp >> (tagSize + parameters.b);
cacheSet set = currentCache.sets[setIndex];
int flag=1;//1 to hit, 0 not;
//simulation hit
for(int i=0;i<parameters.E;i++){
setLine currentLine=set.lines[i];
if(checkHit(currentLine,tag)==1){
parameters.hitNum++;
flag=0;
int tail=checkTail(set, parameters);
set.lines[i].timeStamp = set.lines[tail].timeStamp+1;
}
}
//simulation miss load
if(flag && checkFull(set,parameters)){
parameters.missNum++;
int loadIndex= checkLoad(set,parameters);
set.lines[loadIndex].valid=1;
set.lines[loadIndex].tag=tag;
int tail=checkTail(set,parameters);
set.lines[loadIndex].timeStamp=set.lines[tail].timeStamp+1;
}
else if(flag){
parameters.missNum++;
parameters.evictionNum++;
int evictIndex= checkEvict(set,parameters);
set.lines[evictIndex].valid=1;
set.lines[evictIndex].tag=tag;
int tail= checkTail(set,parameters);
set.lines[evictIndex].timeStamp=set.lines[tail].timeStamp+1;
}
return parameters;
}
- 一些 Simulate() 内的辅助函数 (只给出声明)
int checkHit(setLine line, unsigned long long tag);
int checkFull(cacheSet set, cachePara parameters);
int checkTail(cacheSet set, cachePara parameters);
int checkLoad(cacheSet set, cachePara parameters);
int checkEvict(cacheSet set, cachePara parameters);
(* 完整代码见文末)
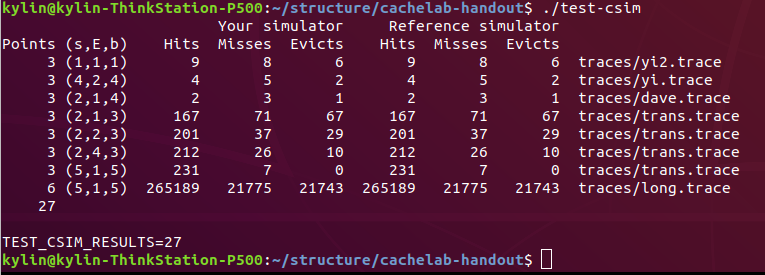
测试结果
执行测试 test-sicm 结果如下:
Part B
- 该部分要求实现一个Cache友好的矩阵转置函数,使Cache Miss次数满足如下条件:
- 32 × 32: 8 points if M < 300, 0 points if M > 600.
- 64 ×64: 8 points if M < 1, 300, 0 points if M > 2, 000.
- 61 ×67: 10 points if M < 2, 000, 0 points if M > 3, 000.
问题分析
- 给定 CacheSize = 1024B,s=5,E=1,b=5。这意味着这是一个直接映射关联 (即单路组关联),而且这个 Cache 每次可以容纳一个Matrix的前8行。
- 将矩阵分成合适大小的块分别求转置可以减少Miss。
- 鉴于可使用变量不超过12个,我们尽量不使用另外的函数调用。而且,在矩阵分块后,块循环与元素循环共需要4个变量,初次之外我们在定义8个临时变量 $tmp1$至 $tmp8$ 。
变量定义如下
//variables init
int row, col;
int rowCheck, colCheck;
int tmp1,tmp2,tmp3,tmp4,tmp5,tmp6,tmp7,tmp8; //temprary variables for exchange two values
具体实现
- 32 x 32
用 8x8 的分块即可实现,但要注意对角线上的元素(此时Matrix A和Matrix B索引到同一个CacheSet,会发生冲突) 要单独拿出来讨论。(代码中仅以N来区别三个测试)
if (N == 32){
for(rowCheck = 0; rowCheck < N; rowCheck += 8)
{
for(colCheck = 0; colCheck < N; colCheck += 8)
{
for(row = rowCheck; row < rowCheck + 8; row++)
{
for(col = colCheck; col < colCheck + 8; col++)
{
if(row != col)
{
B[col][row] = A[row][col];
}
else
{
tmp1 = A[row][col];
tmp2 = row;
}
}
if (rowCheck == colCheck)
{
B[tmp2][tmp2] = tmp1;
}
}
}
}
}
- 61 x 67
由于测试要求比较宽松,而且不规则的matrix不能找到比较显然的规律看出来间隔多少可以填满一个Cache,所以尝试分块大小为16,可以实现要求的2000以下的MIss。
for(rowCheck = 0; rowCheck < N; rowCheck += 16)
{
for(colCheck = 0; colCheck < M; colCheck += 16)
{
for(row = rowCheck; (row < N) && (row < rowCheck + 16); row++)
{
for(col = colCheck; (col < M) && (col < colCheck + 16); col++)
{
if(row != col)
{
B[col][row] = A[row][col];
}
else
{
tmp1 = A[row][col];
tmp2 = row;
}
}
if (rowCheck == colCheck)
{
B[tmp2][tmp2] = tmp1;
}
}
}
}
- 64 x 64
该情况考虑使用 8x8 大小的分块,但是先尽量把Matrix A中尽量多的元素 (4x4的小分块移入Matrix B),之后再在Matrix B中进行元素位置的重新调配。
else if (N == 64){
for(colCheck = 0; colCheck < N; colCheck += 8)
{
for(rowCheck = 0; rowCheck < N; rowCheck += 8)
{
for(row=rowCheck;row<rowCheck+4;++row)
{
tmp1=A[row][colCheck];tmp2=A[row][colCheck+1];tmp3=A[row][colCheck+2];tmp4=A[row][colCheck+3];
tmp5=A[row][colCheck+4];tmp6=A[row][colCheck+5];tmp7=A[row][colCheck+6];tmp8=A[row][colCheck+7];
B[colCheck][row]=tmp1;B[colCheck][row+4]=tmp5;B[colCheck+1][row]=tmp2;B[colCheck+1][row+4]=tmp6;
B[colCheck+2][row]=tmp3;B[colCheck+2][row+4]=tmp7;B[colCheck+3][row]=tmp4;B[colCheck+3][row+4]=tmp8;
}
for(col=colCheck;col<colCheck+4;++col)
{
tmp1=B[col][rowCheck+4];tmp2=B[col][rowCheck+5];tmp3=B[col][rowCheck+6];tmp4=B[col][rowCheck+7];
tmp5=A[rowCheck+4][col];tmp6=A[rowCheck+5][col];tmp7=A[rowCheck+6][col];tmp8=A[rowCheck+7][col];
B[col][rowCheck+4]=tmp5;B[col][rowCheck+5]=tmp6;B[col][rowCheck+6]=tmp7;B[col][rowCheck+7]=tmp8;
B[col+4][rowCheck]=tmp1;B[col+4][rowCheck+1]=tmp2;B[col+4][rowCheck+2]=tmp3;B[col+4][rowCheck+3]=tmp4;
}
for(col=colCheck+4;col<colCheck+8;++col)
{
tmp1=A[rowCheck+4][col];tmp2=A[rowCheck+5][col];tmp3=A[rowCheck+6][col];tmp4=A[rowCheck+7][col];
B[col][rowCheck+4]=tmp1;B[col][rowCheck+5]=tmp2;B[col][rowCheck+6]=tmp3;B[col][rowCheck+7]=tmp4;
}
}
}
}
(* 完整代码见文末)
测试结果
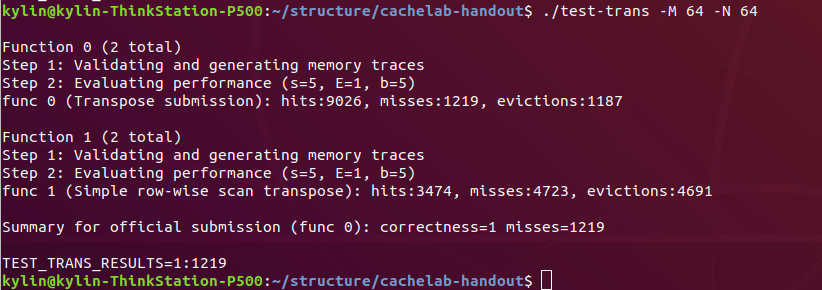
执行测试 test-trans 32 x 32 结果如下:

执行测试 test-trans 64 x 64 结果如下:
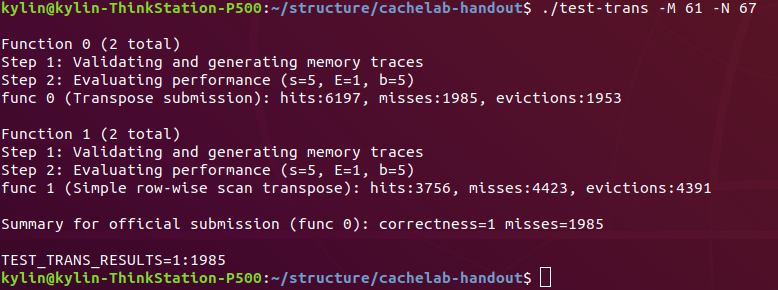
执行测试 test-trans 61 x 67 结果如下:
完整代码
参考我的GitHub:https://github.com/KylinC/CSAPP-Labs