[TOC]
Intro
official notes: https://mlc.ai/chapter_auto_program_optimization/index.html
What’s MLC?
Machine learning compilation (MLC) is the process of transforming and optimizing machine learning execution from its development form to its deployment form.

machine learning compilation still differs from traditional compilation in many ways.
For example, the deployment form can be a set of pre-defined library functions, and the ML compilation only translates the development forms onto calls into those libraries.
Goal of MLC?
- Integration and dependency minimization. 不必要的库就不需要引入了
- Leveraging hardware native acceleration. 利用不同的硬件特性
- Optimization in general. 比如内存、执行效率、分布式等
Key Elements in MLC?
Computation Graph: Tensor, Tensor Function
Abstraction and Implementation
- Abstraction usually allocate in development, whereas Implementation is in deployment
In practice, we usually say that the more specialized version is an implementation of higher-level abstraction。比如说,汇编是一个高层算法的实现。
Key idea of this lesson: Most MLC process can be viewed as transformation among tensor functions (that can be represented with different abstractions)
Four Categories of Abstractions
- Computational Graphs
- Tensor Programs
- Libraries and Runtime
- Hardware Primitives
Tensor Program Abstraction
Primitive Tensor Function
A typical model execution involves several computation steps that transform tensors from input to the final prediction, and each unit step is called a primitive tensor function.
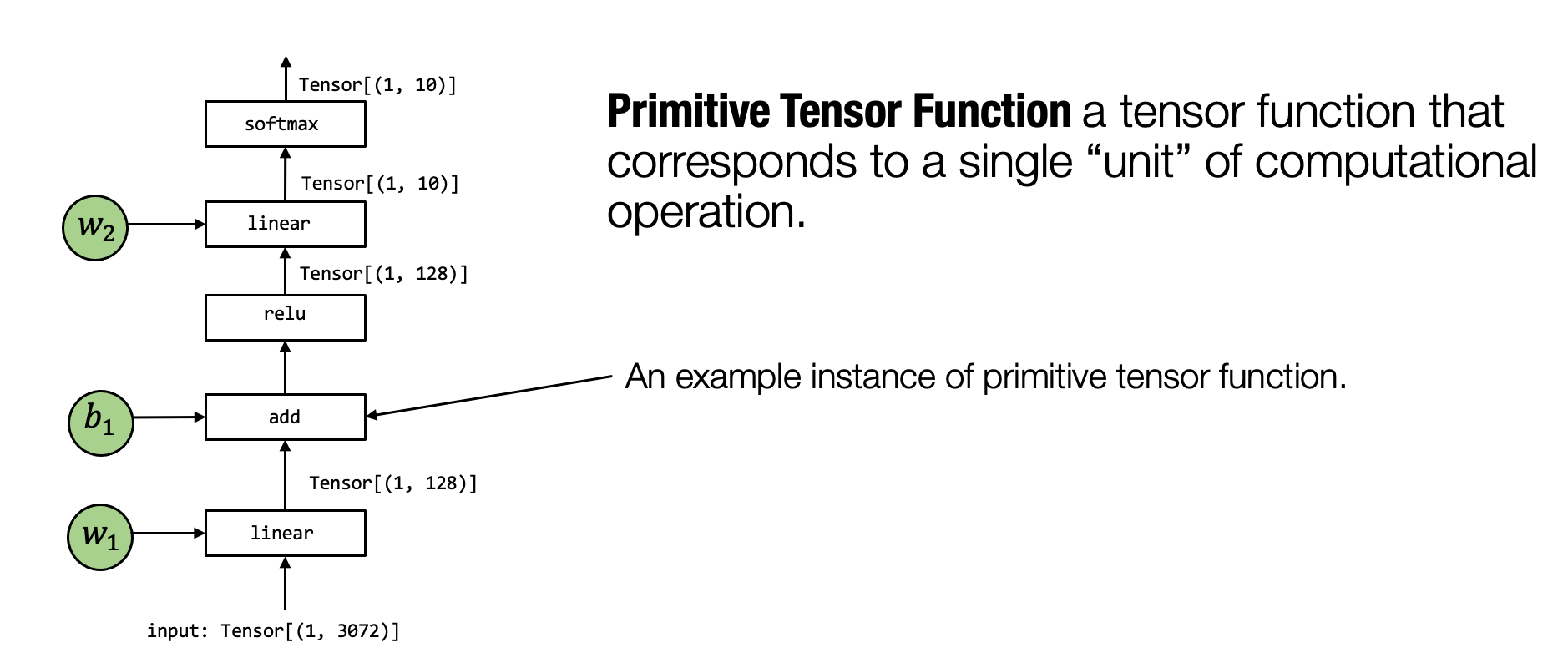
Primitive Function Transformation
One most common MLC process that many frameworks offer is to transform the implementations of primitive functions(or dispatch them in runtime) to more optimized ones based on the environment.
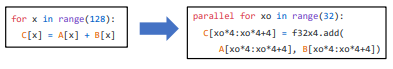
Approaches for primitive function transformation:
- Remap to library calls: e.g. cuda, add => cudaAdd
- Fine-grained program transformation
Tensor Program Transformation
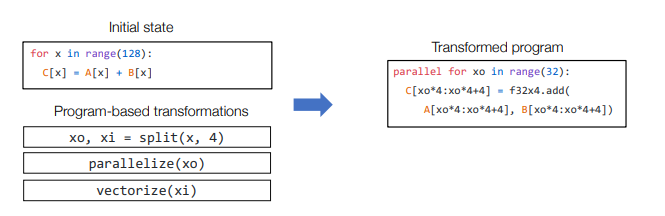
- Key Elements of a Tensor Program
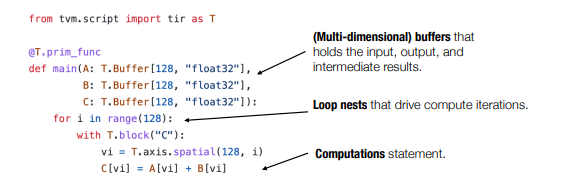
- Example Transformation:
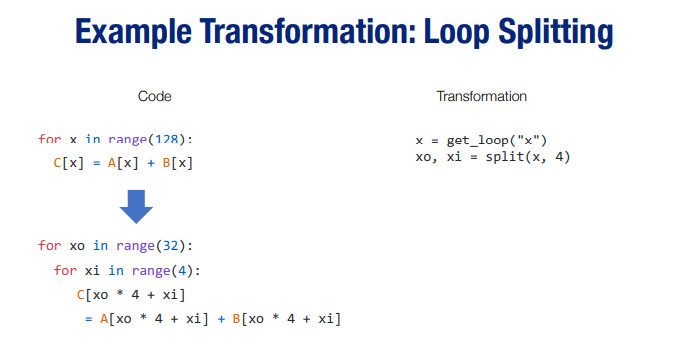
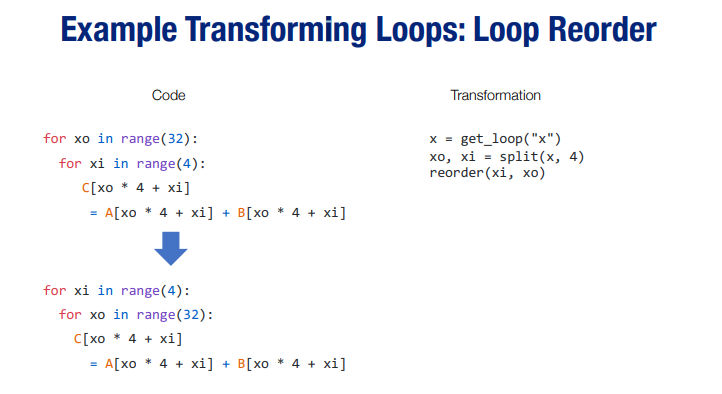
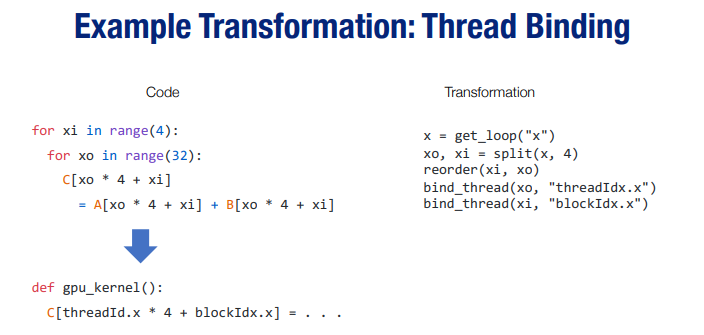
TVM语法相关
- Spatial Aces & Reduce Axes
@tvm.script.ir_module
class MyModule:
@T.prim_func
def mm_relu(A: T.Buffer[(128, 128), "float32"],
B: T.Buffer[(128, 128), "float32"],
C: T.Buffer[(128, 128), "float32"]):
T.func_attr({"global_symbol": "mm_relu", "tir.noalias": True})
Y = T.alloc_buffer((128, 128), dtype="float32")
for i, j, k in T.grid(128, 128, 128):
with T.block("Y"):
vi = T.axis.spatial(128, i)
vj = T.axis.spatial(128, j)
vk = T.axis.reduce(128, k)
with T.init():
Y[vi, vj] = T.float32(0)
Y[vi, vj] = Y[vi, vj] + A[vi, vk] * B[vk, vj]
for i, j in T.grid(128, 128):
with T.block("C"):
vi = T.axis.spatial(128, i)
vj = T.axis.spatial(128, j)
C[vi, vj] = T.max(Y[vi, vj], T.float32(0))
Notably, for a fixed value of vi and vj, the computation block produces a point value at a spatial location of Y (Y[vi, vj]) that is independent from other locations in Y (with a different vi, vj values). we can call vi, vj *spatial axes* as they directly corresponds to the beginning of a spatial region of buffers that the block writes to. The axes that involves in reduction (vk) are named as *reduce axes*.
we can always parallelize over spatial axes, parallelizing over reduce axes will require specific strategies.
- Relax function: high-level NN executions

- Destination passing
The idea is that input and output are explicitly allocated outside and passed to the low-level primitive function. This style is commonly used in low-level library designs, so higher-level frameworks can handle that memory allocation decision. Note that not all tensor operations can be presented in this style (specifically, there are operations whose output shape depends on the input).
def low_level_prim_func(in0, in1, ..., out):
# implementations
- call_tir
隐藏底层的内存分配、以及写输入的操作,使得可以成为一个pure computation graph node
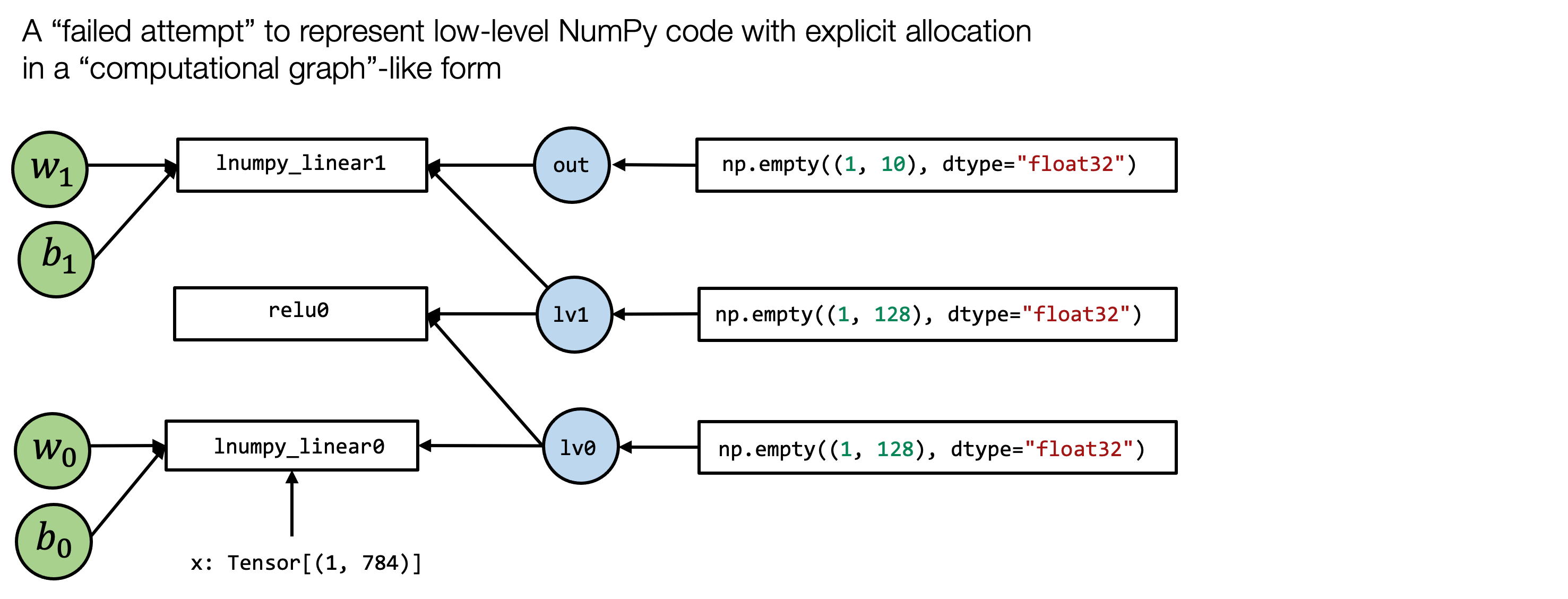
Pure Computational Graph
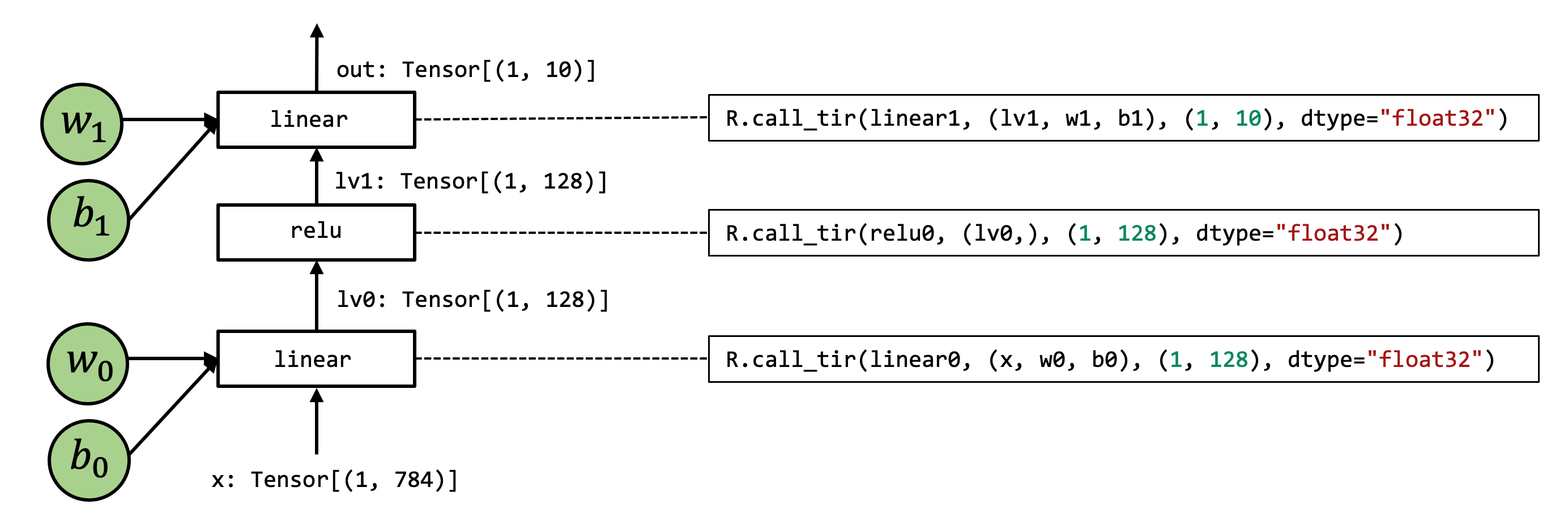
- Dataflow Block
with R.dataflow():
#implement
A dataflow block is a way for us to mark the computational graph regions of the program.
Specifically, within a dataflow block, all the operations need to be side-effect free. Outside a dataflow block, the operations can contain side-effect.
- decompose_reduction
move the initialization of Some_Block’s element separate from the reduction update.
sch.decompose_reduction(block_Y, k)
# 使block_Y的初始化在k相关循环的外面
IPython.display.Code(sch.mod.script(), language="python")
- Automatic Program Optimization

Integrated with Mainstream ML Framework
- BlockBuilder
Build IRModule programmatically
- From torch
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(128, 128))
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.matmul(x, self.weight)
x = torch.relu(x)
return x
model = MyModel()
fx_module = fx.symbolic_trace(model)
# print the graph structure
type(fx_module)
fx_module.graph.print_tabular()
# Create Map Function
#Let us define the overall high-level translation logic. The main flow is as follows:
#- Create a `node_map` that maps `fx.Node` to the corresponding `relax.Var` that #represents the translated node in IRModule.
#- Iterate over the nodes in the fx graph in topological order.
#- Compute the mapped output of the node given the mapped inputs.
def map_param(param: nn.Parameter):
ndim = len(param.data.shape)
return relax.const(
param.data.cpu().numpy(), relax.DynTensorType(ndim, "float32")
)
def fetch_attr(fx_mod, target: str):
"""Helper function to fetch an attr"""
target_atoms = target.split('.')
attr_itr = fx_mod
for i, atom in enumerate(target_atoms):
if not hasattr(attr_itr, atom):
raise RuntimeError(f"Node referenced nonexistant target {'.'.join(target_atoms[:i])}")
attr_itr = getattr(attr_itr, atom)
return attr_itr
def from_fx(fx_mod, input_shapes, call_function_map, call_module_map):
input_index = 0
node_map = {}
named_modules = dict(fx_mod.named_modules())
bb = relax.BlockBuilder()
fn_inputs = []
fn_output = None
with bb.function("main"):
with bb.dataflow():
for node in fx_mod.graph.nodes:
if node.op == "placeholder":
# create input placeholder
shape = input_shapes[input_index]
input_index += 1
input_var = relax.Var(
node.target, shape, relax.DynTensorType(len(shape), "float32")
)
fn_inputs.append(input_var)
node_map[node] = input_var
elif node.op == "get_attr":
node_map[node] = map_param(fetch_attr(fx_mod, node.target))
elif node.op == "call_function":
node_map[node] = call_function_map[node.target](bb, node_map, node)
elif node.op == "call_module":
named_module = named_modules[node.target]
node_map[node] = call_module_map[type(named_module)](bb, node_map, node, named_module)
elif node.op == "output":
output = node_map[node.args[0]]
assert fn_output is None
fn_output = bb.emit_output(output)
# output and finalize the function
bb.emit_func_output(output, fn_inputs)
return bb.get()
# how we use
def map_matmul(bb, node_map, node: fx.Node):
A = node_map[node.args[0]]
B = node_map[node.args[1]]
return bb.emit_te(te_matmul, A, B)
def map_relu(bb, node_map, node: fx.Node):
A = node_map[node.args[0]]
return bb.emit_te(te_relu, A)
MyModule = from_fx(
fx_module,
input_shapes = [(1, 128)],
call_function_map = {
torch.matmul: map_matmul,
torch.relu: map_relu,
},
call_module_map={},
)
MyModule.show()
GPU and Specialized Hardware
Arch
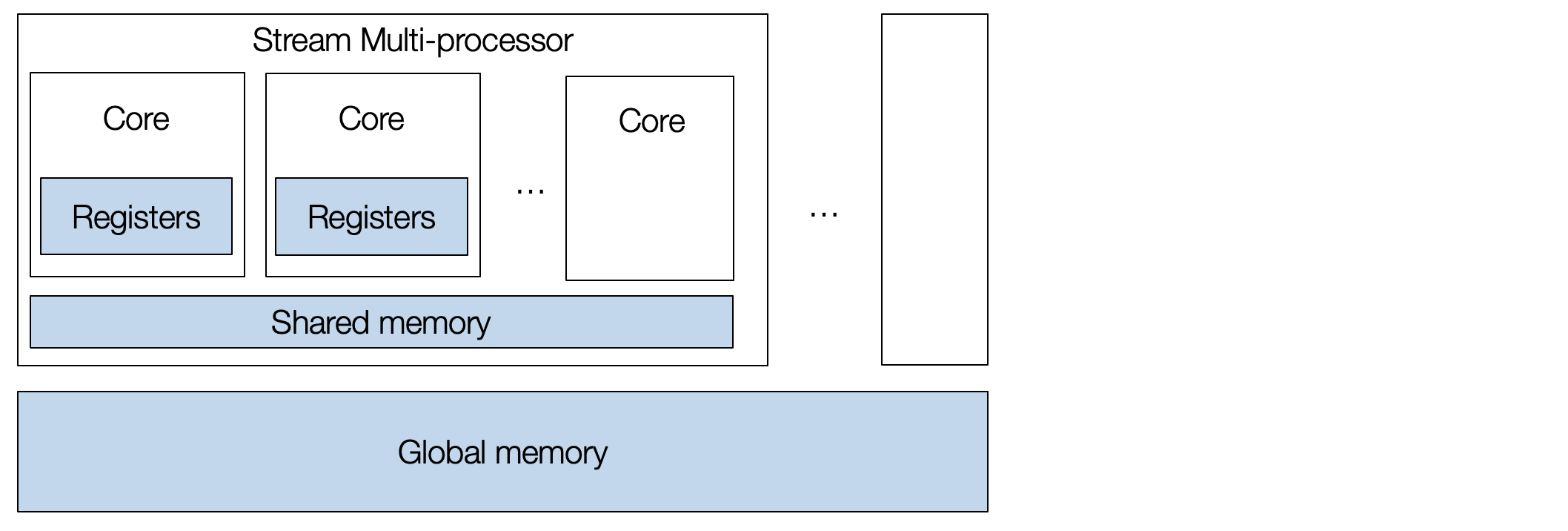
Programming Arch

eg. Conv1d
- cooperative fetching
https://mlc.ai/chapter_gpu_acceleration/part1.html#window-sum-example
eg. GEMM
- Local Blocking
https://mlc.ai/chapter_gpu_acceleration/part1.html#matrix-multiplication
- Shared Memory Blocking
https://mlc.ai/chapter_gpu_acceleration/part1.html#shared-memory-blocking
Graph Optimization
- IRModule Data Structure (AST)
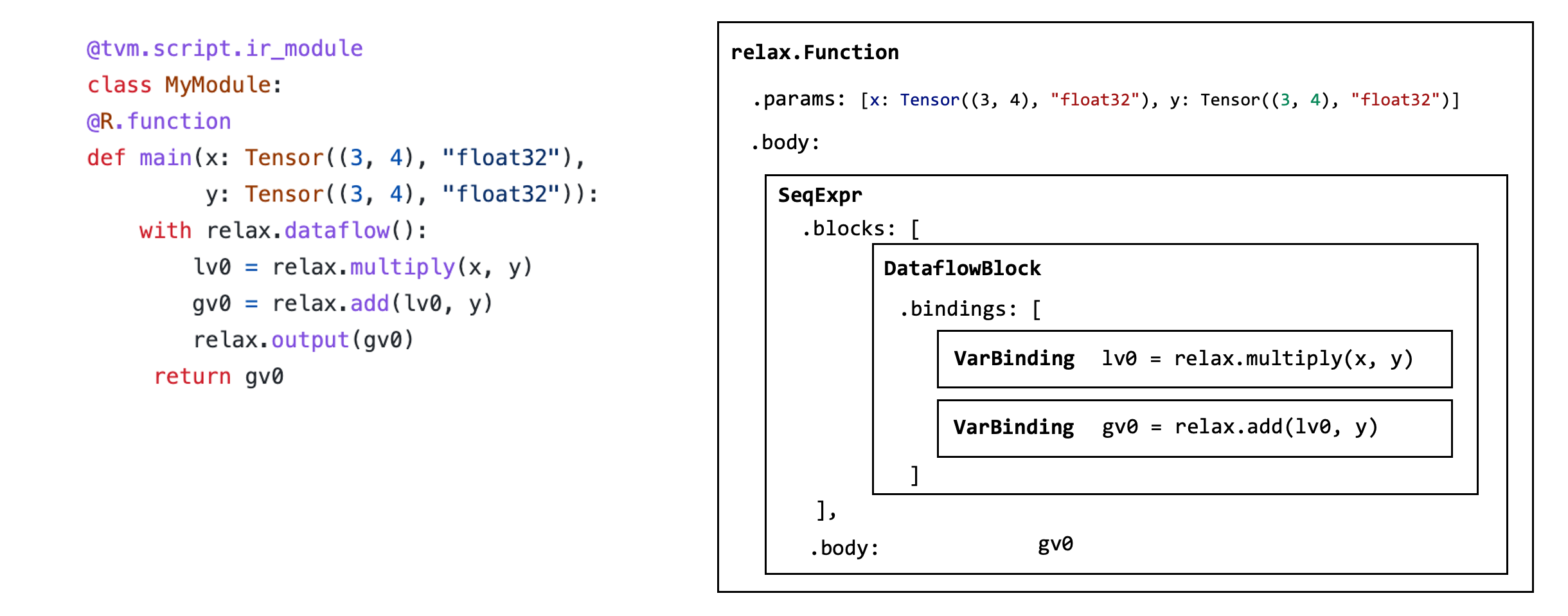
- use Visit Pattern to transform Computational Graph
待修改graph
@tvm.script.ir_module
class MyModule:
@R.function
def main(x: R.Tensor((3, 4), "float32"), y: R.Tensor((3, 4), "float32")):
with R.dataflow():
lv0 = relax.op.multiply(x, y)
gv0 = relax.op.add(lv0, y)
R.output(gv0)
return gv0
修改函数
@relax.expr_functor.mutator
class EwiseFMARewriter(relax.PyExprMutator):
def visit_call_(self, call):
call = self.visit_expr_post_order(call)
add_op = tvm.ir.Op.get("relax.add")
multiply_op = tvm.ir.Op.get("relax.multiply")
ewise_fma_op = tvm.ir.Op.get("relax.ewise_fma")
if call.op != add_op:
return call
value = self.lookup_binding(call.args[0])
if not isinstance(value, relax.Call) or value.op != multiply_op:
return call
fma_call = relax.Call(
ewise_fma_op, [value.args[0], value.args[1], call.args[1]], None, None
)
return fma_call
updated_fn = EwiseFMARewriter().visit_expr(MyModule["main"])
updated_fn.show()
修改!
relax.analysis.remove_all_unused(updated_fn).show()
- Map to high-level Intrinsic
https://mlc.ai/chapter_graph_optimization/index.html#
@relax.expr_functor.mutator
class DenseAddFusor(relax.PyExprMutator):
def __init__(self, mod: IRModule) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.mod_ = mod
# cache pre-defined ops
self.add_op = tvm.ir.Op.get("relax.add")
self.dense_op = tvm.ir.Op.get("relax.nn.dense")
self.counter = 0
def transform(self) -> IRModule:
for global_var, func in self.mod_.functions.items():
if not isinstance(func, relax.Function):
continue
# avoid already fused primitive functions
if "Primitive" in func.attrs.keys() and func.attrs["Primitive"] != 0:
continue
updated_func = self.visit_expr(func)
updated_func = relax.analysis.remove_all_unused(updated_func)
self.builder_.update_func(global_var, updated_func)
return self.builder_.get()
def visit_call_(self, call):
call = self.visit_expr_post_order(call)
def match_call(node, op):
if not isinstance(node, relax.Call):
return False
return node.op == op
# pattern match dense => add
if not match_call(call, self.add_op):
return call
value = self.lookup_binding(call.args[0])
if value is None:
return call
if not match_call(value, self.dense_op):
return call
x = value.args[0]
w = value.args[1]
b = call.args[1]
# construct a new fused primitive function
param_x = relax.Var("x", x.shape_, x._checked_type_)
param_w = relax.Var("w", w.shape_, w._checked_type_)
param_b = relax.Var("b", b.shape_, b._checked_type_)
bb = relax.BlockBuilder()
fn_name = "fused_dense_add%d" % (self.counter)
self.counter += 1
with bb.function(fn_name, [param_x, param_w, param_b]):
with bb.dataflow():
lv0 = bb.emit(relax.op.nn.dense(param_x, param_w))
gv = bb.emit_output(relax.op.add(lv0, param_b))
bb.emit_func_output(gv)
# Add Primitive attribute to the fused funtions
fused_fn = bb.get()[fn_name].with_attr("Primitive", 1)
global_var = self.builder_.add_func(fused_fn, fn_name)
# construct call into the fused function
return relax.Call(global_var, [x, w, b], None, None)
@tvm.ir.transform.module_pass(opt_level=2, name="DeseAddFuse")
class FuseDenseAddPass:
"""The wrapper for the LowerTensorIR pass."""
def transform_module(self, mod, ctx):
return DenseAddFusor(mod).transform()
MLPFused = FuseDenseAddPass()(MLPModel)
MLPFused.show()
- Map to low-level IRModule
@relax.expr_functor.mutator
class LowerToTensorIR(relax.PyExprMutator):
def __init__(self, mod: IRModule, op_map) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.mod_ = mod
self.op_map = {
tvm.ir.Op.get(k): v for k, v in op_map.items()
}
def visit_call_(self, call):
call = self.visit_expr_post_order(call)
if call.op in self.op_map:
return self.op_map[call.op](self.builder_, call)
return call
def transform(self) -> IRModule:
for global_var, func in self.mod_.functions.items():
if not isinstance(func, relax.Function):
continue
updated_func = self.visit_expr(func)
self.builder_.update_func(global_var, updated_func)
return self.builder_.get()
def map_matmul(bb, call):
x, w = call.args
return bb.call_te(topi.nn.matmul, x, w)
def map_add(bb, call):
a, b = call.args
return bb.call_te(topi.add, a, b)
def map_relu(bb, call):
return bb.call_te(topi.nn.relu, call.args[0])
def map_transpose(bb, call):
return bb.call_te(topi.transpose, call.args[0], )
op_map = {
"relax.matmul": map_matmul,
"relax.add": map_add,
"relax.nn.relu": map_relu,
"relax.permute_dims": map_transpose
}
@tvm.ir.transform.module_pass(opt_level=0, name="LowerToTensorIR")
class LowerToTensorIRPass:
"""The wrapper for the LowerTensorIR pass."""
def transform_module(self, mod, ctx):
return LowerToTensorIR(mod, op_map).transform()
MLPModelTIR = LowerToTensorIRPass()(MLPFused)
MLPModelTIR.show()
Future Work
- Framework of MLC
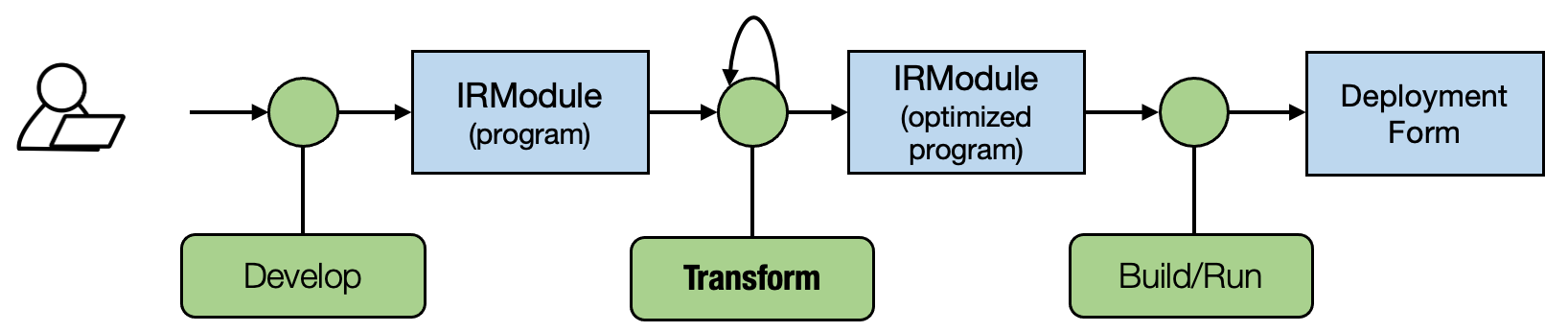
- Example MLC Process
TensorIR-level transformations among primitive tensor functions.
Computational graph transformations: operator fusion.
Mapping to library functions
- Future Directions
Feedback and cross-layer optimizations.
Smarter automatic approaches for specialized hardware.
Collaboration between engineers and compilation system