[TOC]
This work demonstrate that model parallelism can be additionally used for the statistical multiplexing of multiple devices when serving multiple models, even when a single model can fit into a single device.
represent a system, AlpaServe, that determines an efficient strategy for placing and parallelizing collections of large deep learning models across a distributed cluster.
Motivation: alpa做的事情本质上都是把一个模型放在多张卡上(无论是intra-op还是inter-op),因此 we can fit more models on one device, enabling better statistical multiplexing of the devices when handling bursty requests.
不同的模型放置方式会产生不同的latency,this picture is great(两个GPU,部署两个模型,服务6个模型推理访问请求):
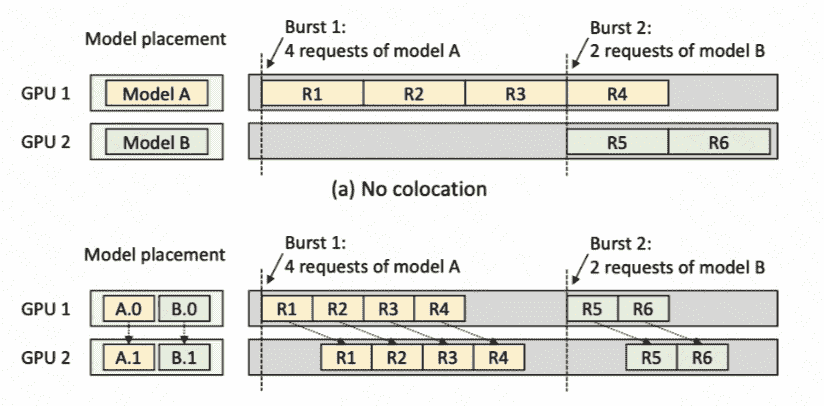
- Service有一个特点,就是有burst,而且burst请求负载大概在空闲的50x以上。
- SLO:service level objective。一个alpa内的重要metrics:SLO attainment (i.e., the percentage of requests served within SLO)
Case Study
two GPUs to serve two Transformer models with 6.7 billion parameters each (13.4 GB to store its FP16 weights). Because each GPU has 16 GB of memory, it can fit one and only one model. A single request takes around 0.4 s to process on one GPU.
之后用不同的请求分布进行模拟,利用latency的累积分布函数进行评价:
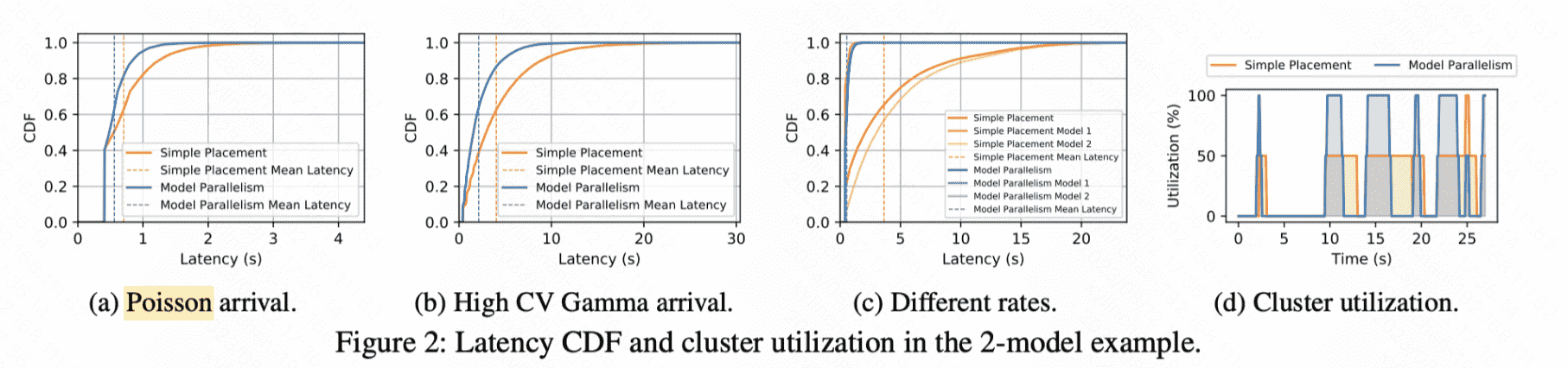
第三个图是模拟了对两个GPU不同全球权重的模拟,还是利用柏松分布,但是对于No colocation来讲,GPU1处理20%请求,GPU2处理80%请求(对于model parallel来说,不能分GPU请求,因为就是一个流水线)
发现:轻请求的时候 model parallel 效果不好,因为存在通信开销
Algorithm
两个重点:
- 如何划分模型(partition)
- 如何指派模型块到设备(placement)
Experiment
setup
设备:8 nodes and 64 GPUs. Each node is an AWS EC2 p3.16xlarge instance with 8 NVIDIA Tesla V100 (16GB) GPUs.
模型:BERT [12] and GShard MoE(作者认为反正LLM都是transformer,找两个有代表性的就好)
metrics
- SLO attainment (major)
在给定的SLOa下:
- (1) the minimal number of devices the system needs
- (2) the maximum average request rate
- (3) the maximum traffic burstiness the system can support
- (4) the minimal SLO the system can handle.
注意到实验是在一个模拟器上完成的,虽然paper说实现了一个姿势系统: 启动多个alpa运行时,并通过控制器指派任务