[TOC]
ICML 2023
Motivation:
high-throughput LLM inference using limited resources, such as a single and commodity GPU.
throughput-oriented generative inference
Background:
现有的资源受限LLM inference的work主要分做三个类:
1)模型压缩(可能是量化?)
2)分布式推理(论文原话: collaborative inference via decentralization)
3)offloading to CPU and disk
但是 FlexGen 说前两个都是只用GPU-Mem的,所以不能用很大的模型
而最后一个可能因为 inefficient I/O scheduling 和 tensor placement 导致带宽低
Contribution:
- 给出了一个offloading strategies的搜索策略(考虑 computation schedule, tensor placement, computation delegation),可以做到2x最优
- 给出了一个适合FlexGen的量化方法
- 做了和DeepSpeed Zero-Inference、Hugging Face Accelerate的对比实验
Background
- Generative Inference 和 Transformer.forward是有很大区别的,关键在于KV Cache上,一般对于very LLM来说,KV cache会比其权重还要大 ref.
In a realistic setting with a sufficient number of GPUs, the OPT-175B model (l = 96, h1= 12288, h2= 49152) takes 325 GB. With a batch size of b = 512, an input sequence length s = 512, and an output sequence length of n = 32, the total memory required to store the KV cache is 1.2 TB, which is 3.8× the model weights, making the KV cache a new bottleneck of large-batch high-throughput inference.
Considering the OPT-175B model in FP 16, the total number of bytes to store the parameters can be roughly calculated by $l\left(8 h_1^2+4 h_1 h_2\right)$. The total number of bytes to store the KV cache in peak is $4 \times b l h_1(s+n)$.
Offloading Strategy
两个步骤:
1) builds an analytical cost model 2) searches for configurations with an optimizer based on linear programming. 3) (Extra) show how to extend FlexGen to support multi-GPU settings.
Formulation
把 generation 问题建模成 graph travel 问题:
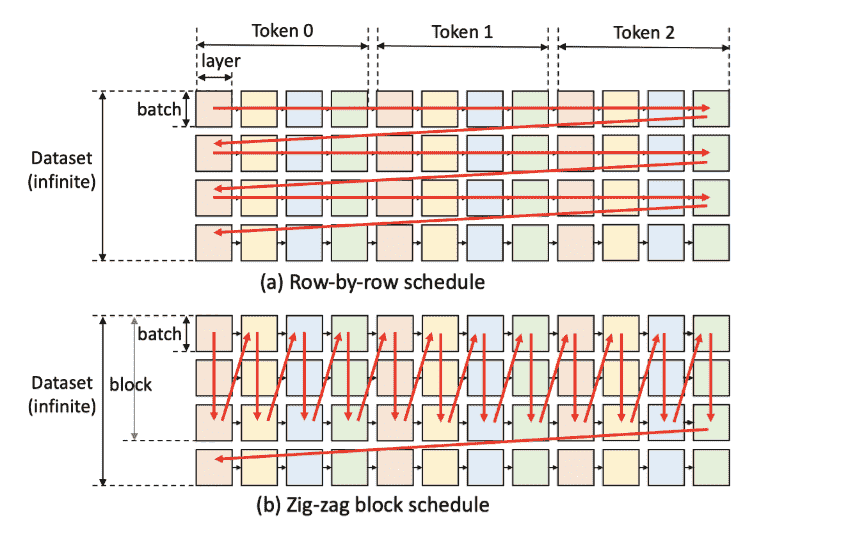
这里不同颜色代表不同层,模拟的是batch_size = 4, 生成 3 token 的场景。
constraint:
- A square can only be computed if all squares to its left on the same row were computed.
- To compute a square on a device, all its inputs (weights, activations, cache) must be loaded to the same device.
- After being computed, a square produces two outputs: activations and KV cache. The activations should be stored until its right sibling is computed. The KV cache should be stored until the rightmost square on the same row is computed.
- At any time, the total size of tensors stored on a device cannot exceed its memory capacity.
Search Space
- compute schedule
optimization 1: Zig-Zag travel (文章证明了这个方案是 2x 最优的)
optimization 2: Overlapping
- Tensor placement
粒度问题:Considering both the runtime overhead and desired flexibility, we use layer granularity for weights, and tensor granularity for activations and the KV cache.
引入约束变量限制在三级储存中的百分比。
- Computation delegation
有的时候在在KV cache储存近端进行计算是最优的:
KV cache 存在 DRAM,在CPU计算后把activation -> GPU 的字节为 $b\times h_1 \times 4$
或者 KV cache -> GPU 字节为 $s \times b\times h_1 \times 4$
Cost Model
FlexGen的cost是通过数学进行估计的
做一个block推理的lantency估计为(注意一个block中的纵列的layer只需要load一次,即zig-zag): \(T=T_{p r e} \cdot l+T_{g e n} \cdot(n-1) \cdot l\)
其中 T_pre 为load一个layer的延迟,T_gen 为推理完一个block_batch的一层的延迟,所以paper认为T_gen会更大
而这里的延迟是使用bits/bandwidth方式估计出来的。
除此之外,FlexGen还估计了内存占用以添加内存约束
Policy Search
确定一组 (bls, gbs) 即 (block_size, batch_size),其中 bls 是4的倍数,gbs小于20,然后搜索tensor placement:
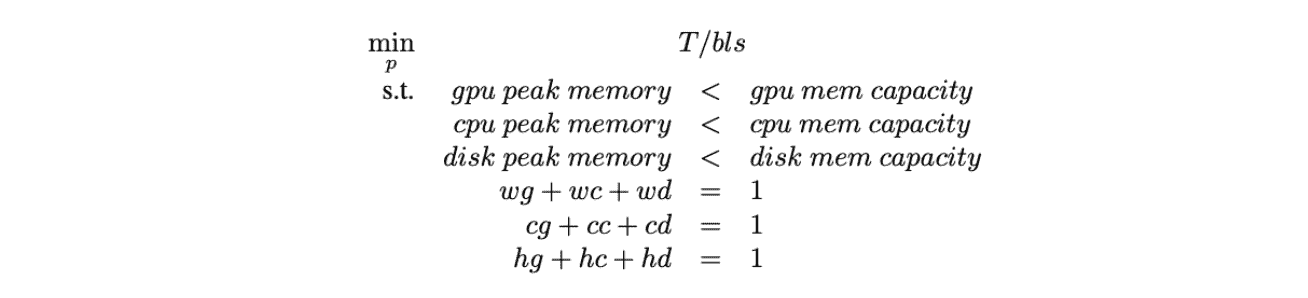
然后说如果坏了只能手调,而且手调的还好hhh
(Extra) Extension to Multiple GPUs
就是平均分layer到stage,不考虑device计算性能
Approximate Methods
For Better Inference Throughput
Evaluation
setup
Google Cloud NVIDIA T4 GPU
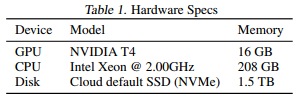
The read bandwidth of SSD is about 2GB/s and the write bandwidth is about 1GB/s.
Metrics
Throughput and Latency:
def. Considering an effective batch size $b$, an input sequence length $s$, and an output sequence length of $n$, the latency $t$ is defined as the total number of seconds spent to process the prompts and generate all the $b n$ tokens. The generation throughput is defined as $b n / t$ token/s.
Baseline
DeepSpeed ZeRO-Inference
Hugging Face Accelerate
Petals (decentralized collaborative inference)