[TOC]
vLLM Document:https://vllm.readthedocs.io/en/latest/serving/distributed_serving.html
vLLM utilizes PagedAttention, our new attention algorithm that effectively manages attention keys and values.
- Result: vLLM achieves up to 24x higher throughput compared to HF and up to 3.5x higher throughput than TGI.
Paged Attention
下面这番表述可以好好学一下:
we identify that the performance of LLM serving is bottlenecked by memory. In the autoregressive decoding process, all the input tokens to the LLM produce their attention key and value tensors, and these tensors are kept in GPU memory to generate next tokens. These cached key and value tensors are often referred to as KV cache. The KV cache is
- Large: Takes up to 1.7GB for a single sequence in LLaMA-13B.
- Dynamic: Its size depends on the sequence length, which is highly variable and unpredictable. As a result, efficiently managing the KV cache presents a significant challenge. We find that existing systems waste 60% – 80% of memory due to fragmentation and over-reservation.
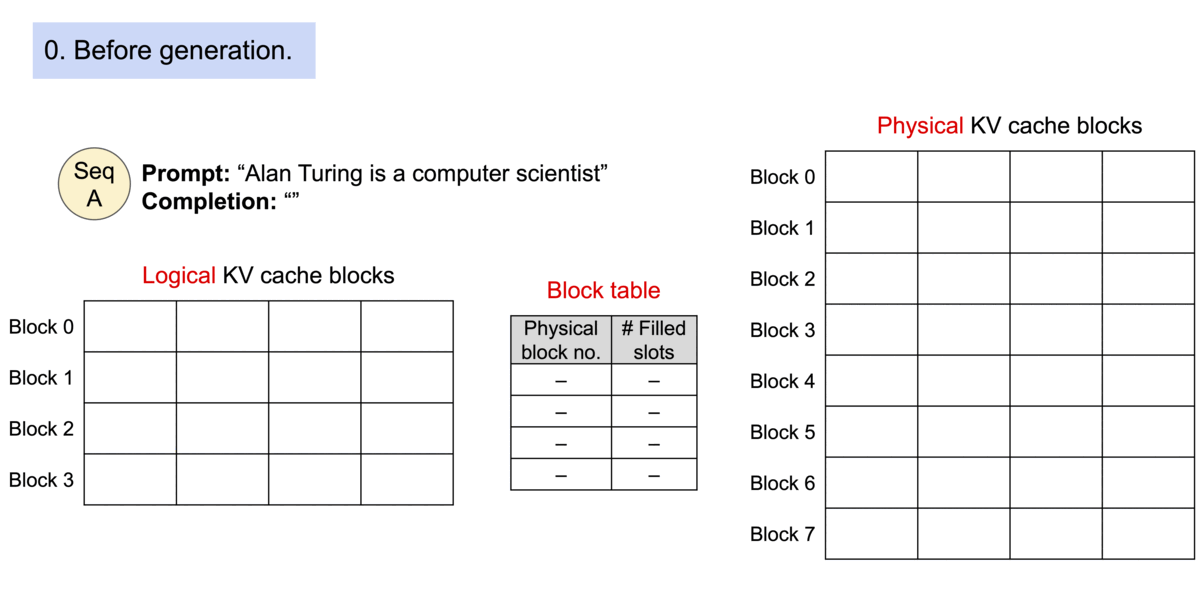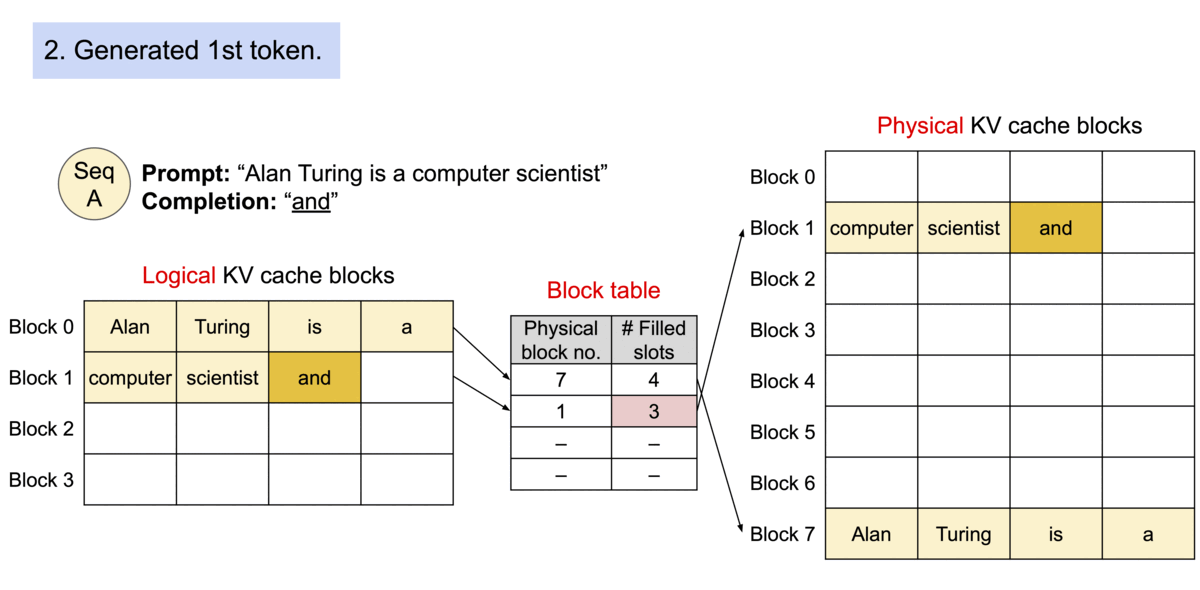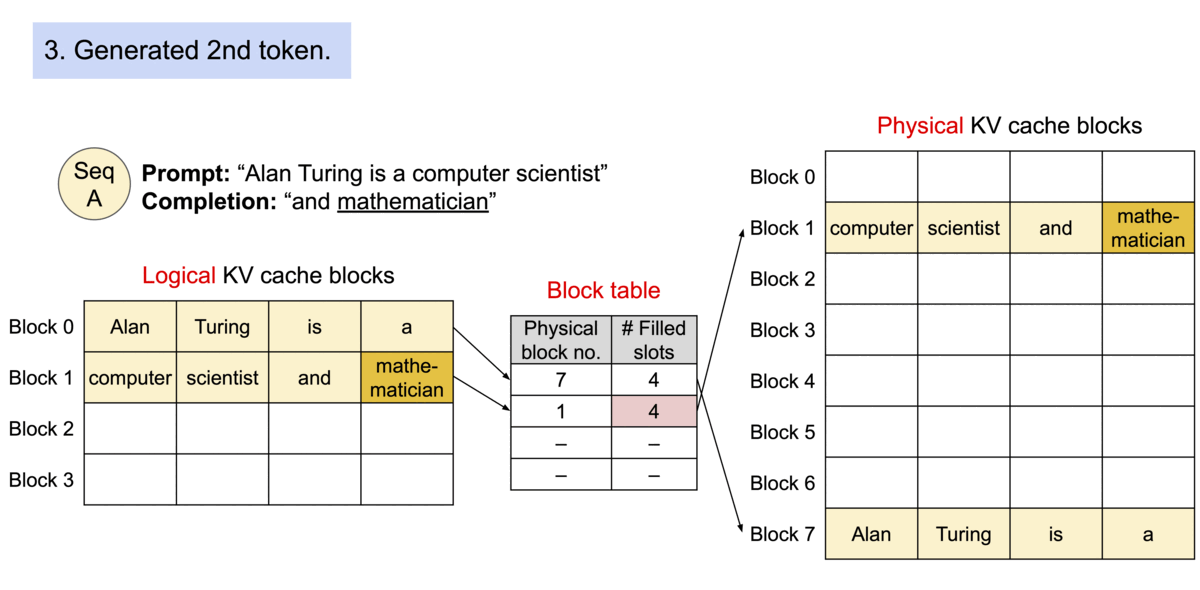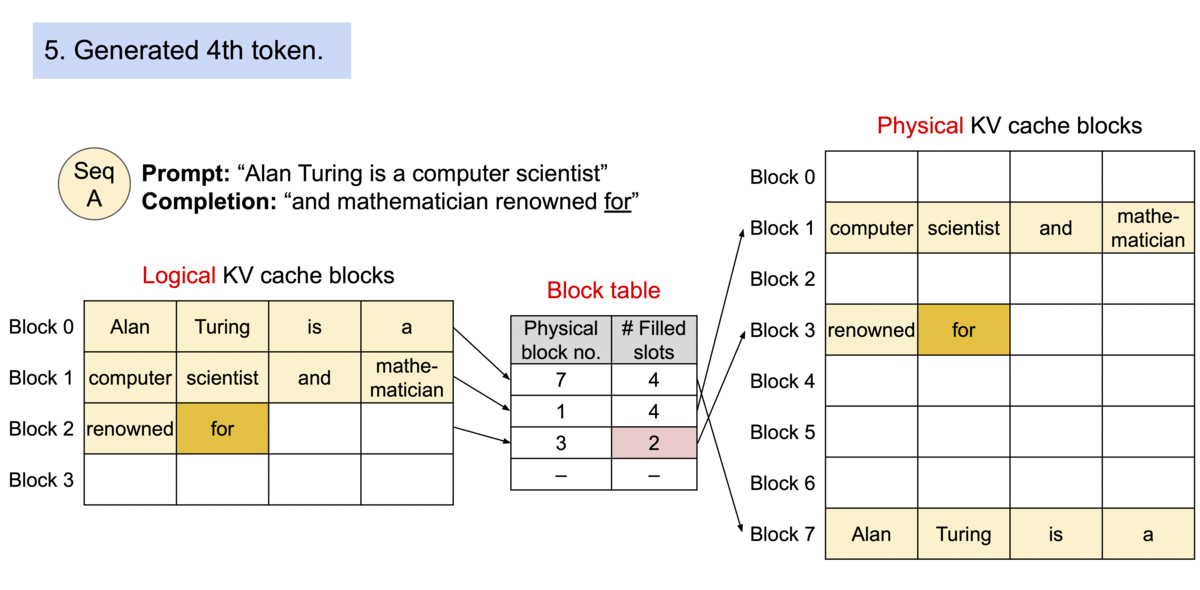
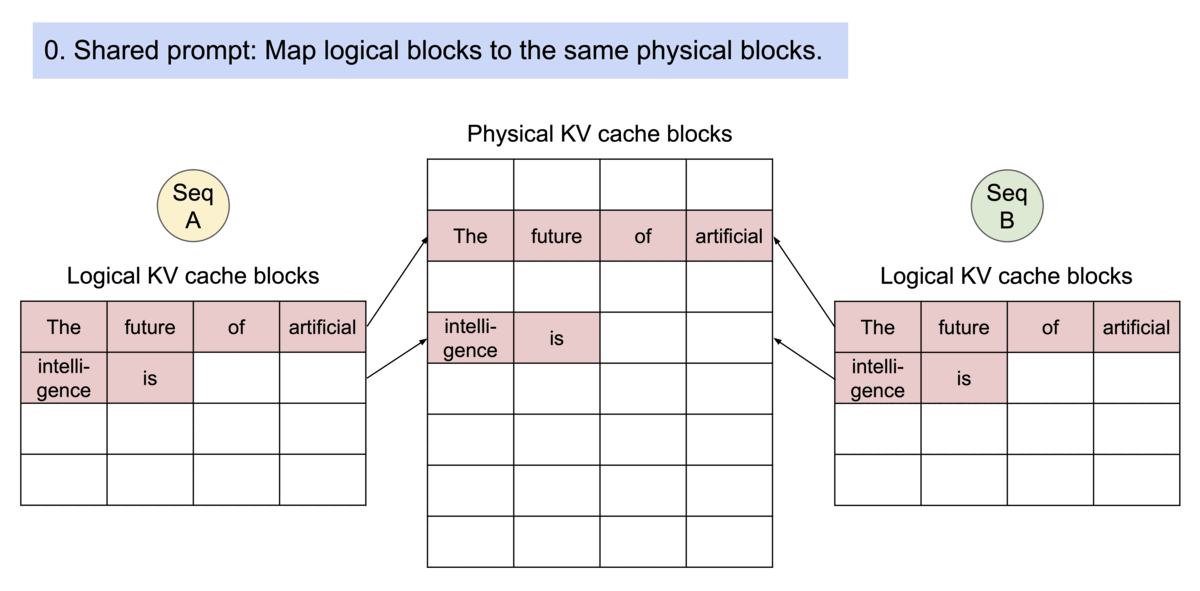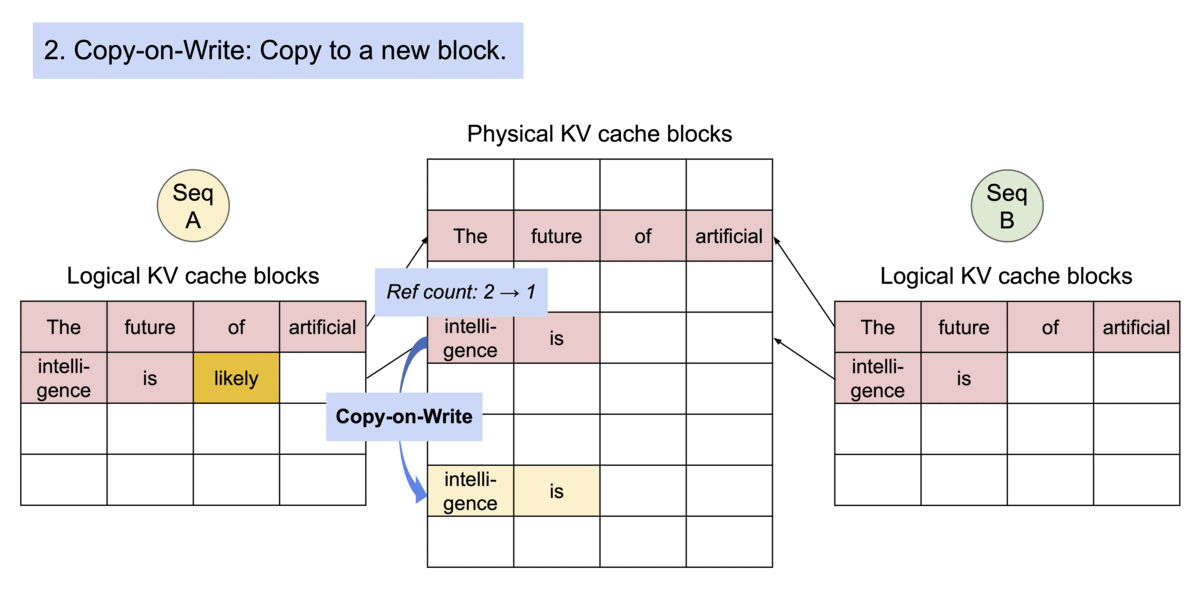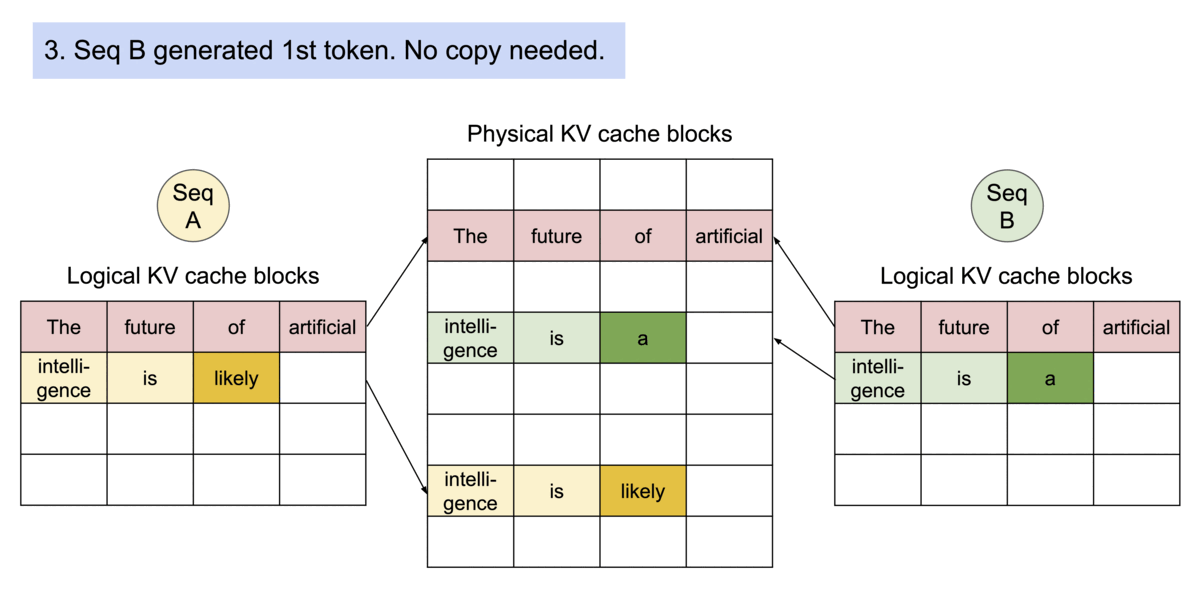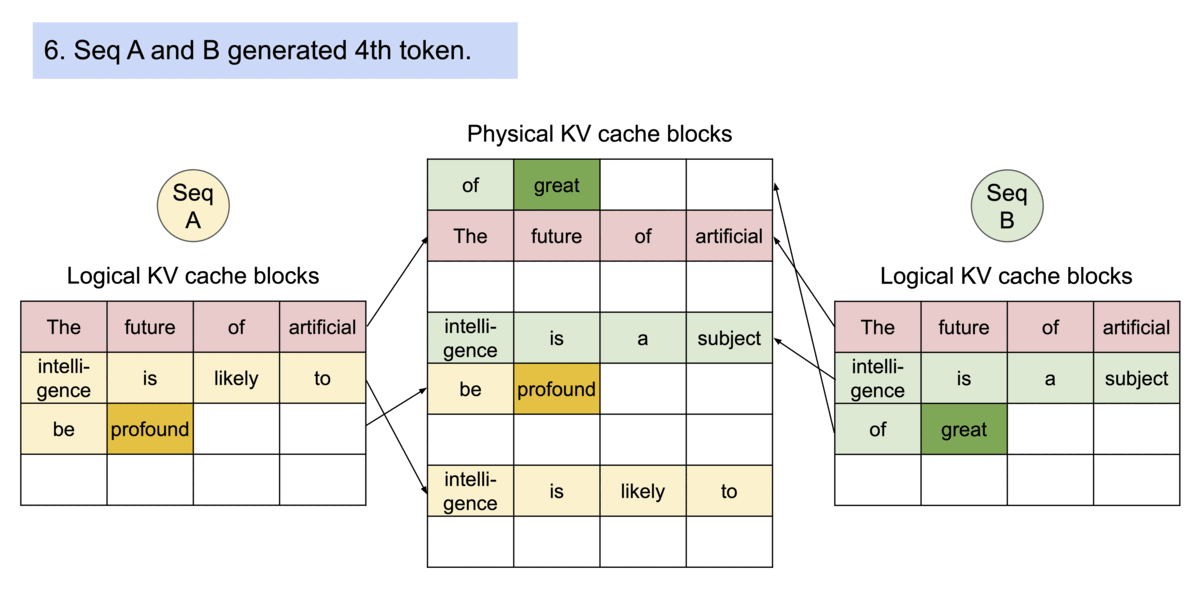
Key idea: PagedAttention allows storing continuous keys and values in non-contiguous memory space.
Specifically, PagedAttention partitions the KV cache of each sequence into blocks, each block containing the keys and values for a fixed number of tokens. During the attention computation, the PagedAttention kernel identifies and fetches these blocks efficiently.
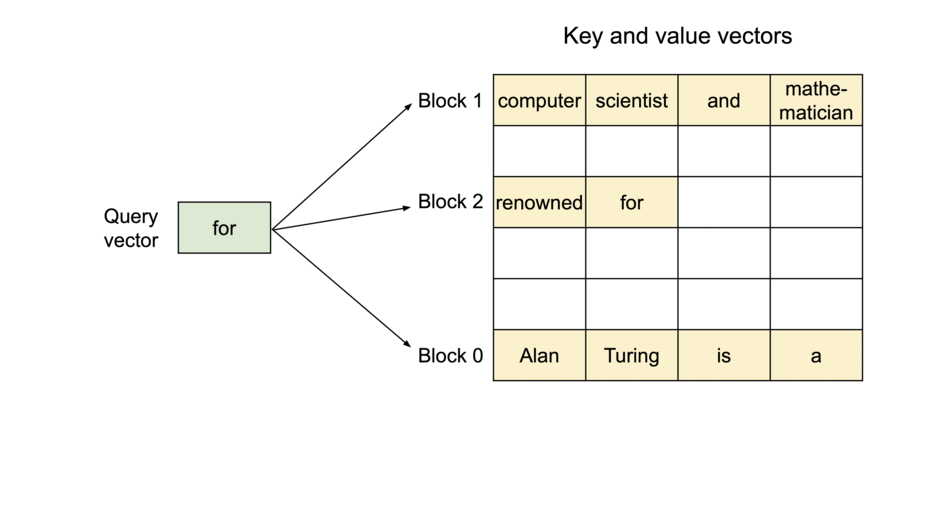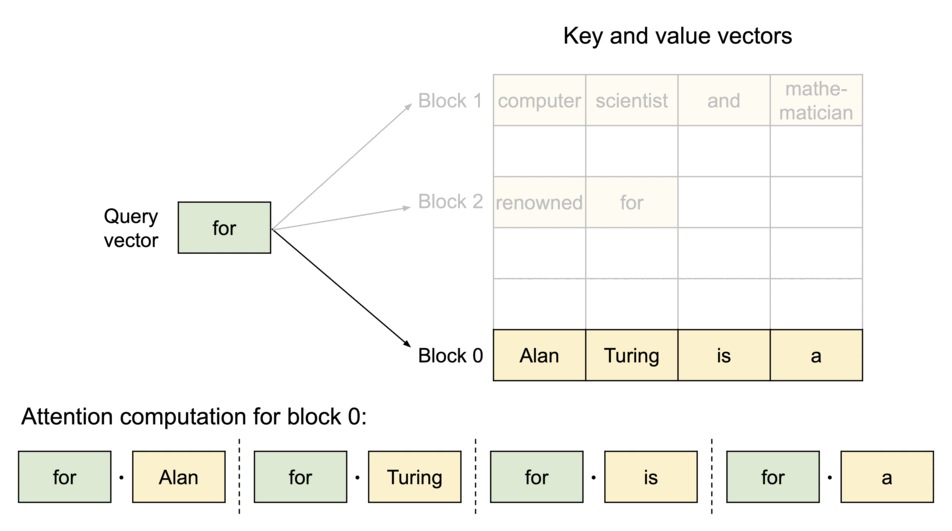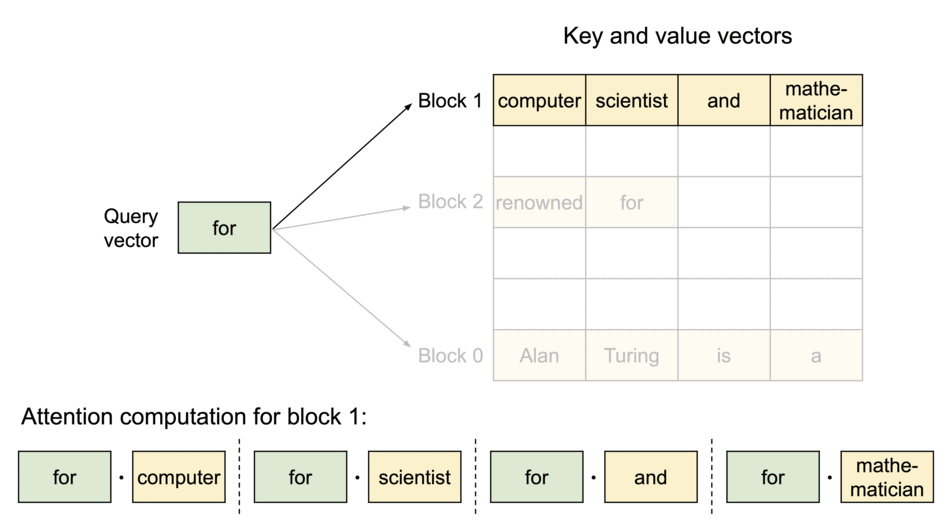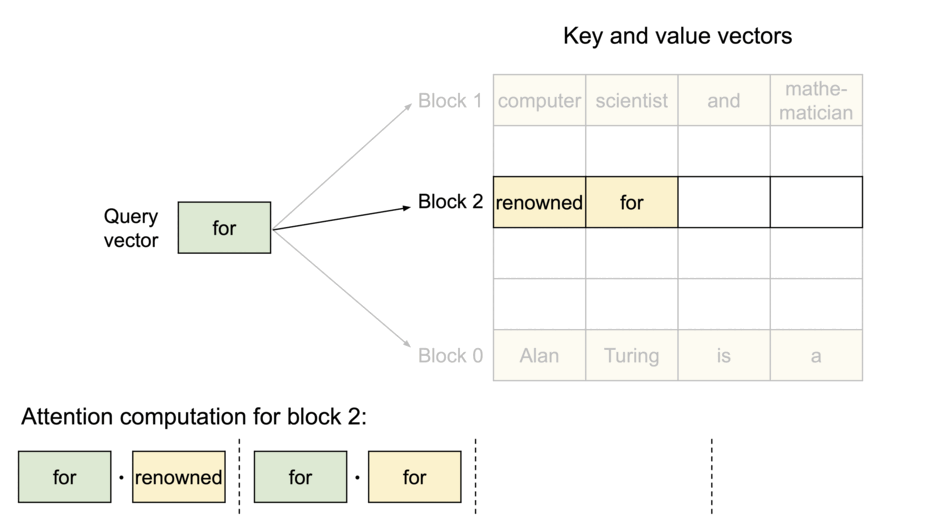
Block Table
Sample Optimization
可以结合beamsearch在较小储存开销下生成更好的generation。
Experiment
Baselines
HuggingFace Text Generation Inference (TGI)
Setups
LLaMA-7B on an NVIDIA A10G GPU
LLaMA-13B on an NVIDIA A100 GPU (40GB)
We sample the requests’ input/output lengths from the ShareGPT dataset
Result
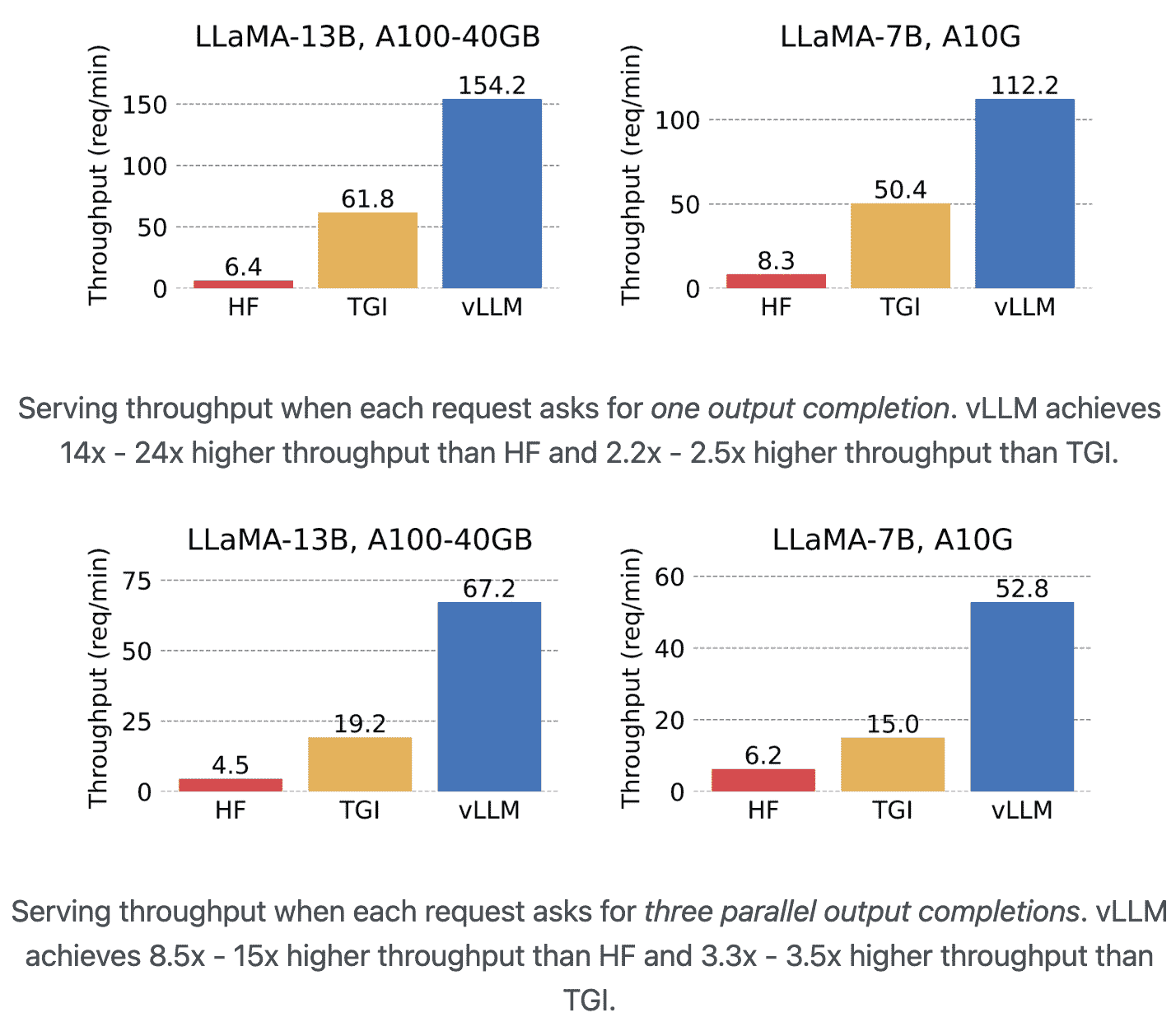
Rethink
Nvidia关于 memory-bounded的叙述:https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/performance/dl-performance-gpu-background/index.html#understand-perf