Lil’Log What are Diffusion Models?
[TOC]
limitations
- GAN:unstable training and less diversity in generation due to their adversarial training nature.
- VAE:relies on a surrogate loss.
- Flow-based models:have to use specialized architectures to construct reversible transform.
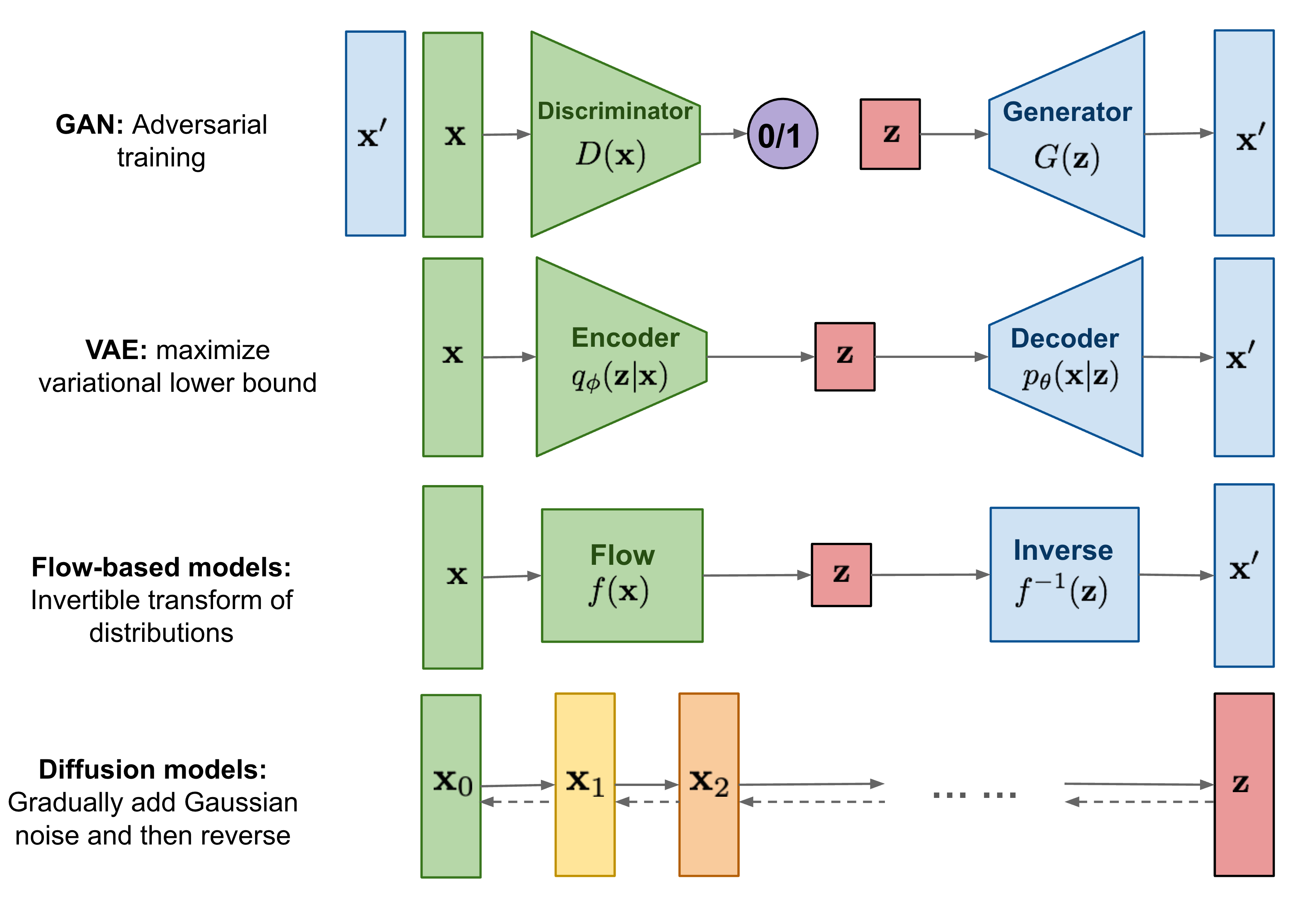
Basics
基于马尔可夫假说的联合条件概率,图片和随机噪声之间可以建模成一个可逆的过程
The Markov chain of forward (reverse) diffusion process of generating a sample by slowly adding (removing) noise:
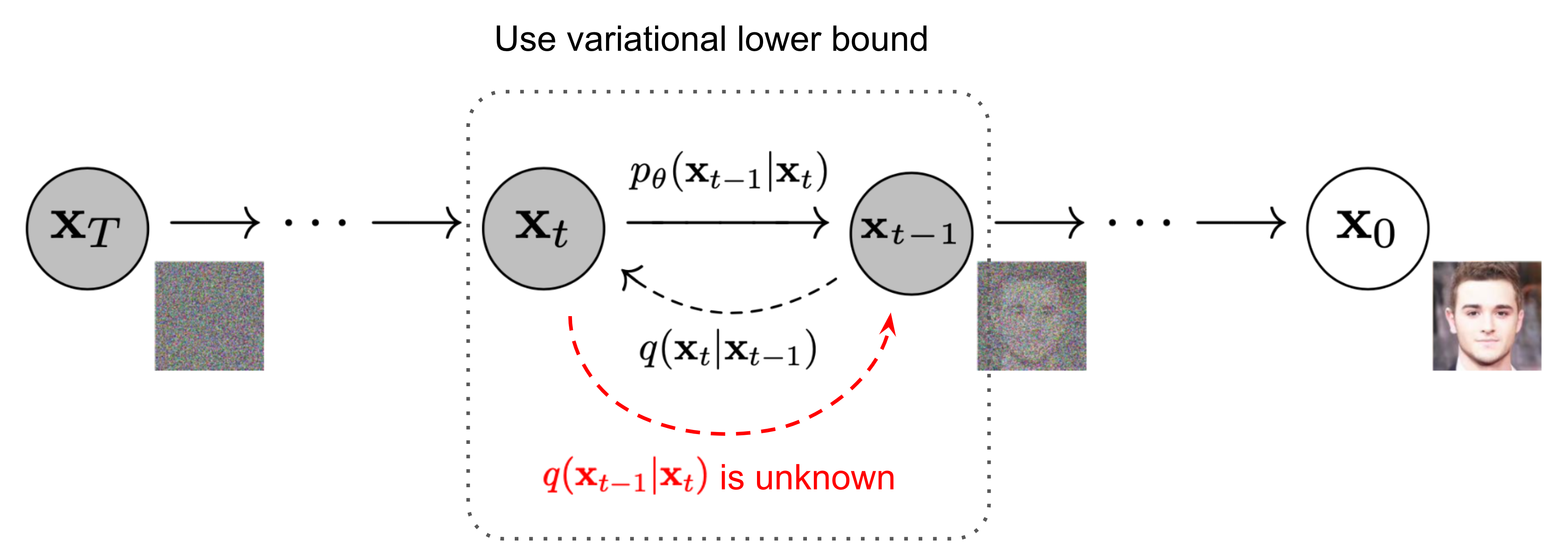
diffusion model要解决的一个关键问题就是如何从随机噪声中逐步恢复图片1: \(p_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_{0: T}\right)=p\left(\mathbf{x}_T\right) \prod_{t=1}^T p_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_{t-1} \mid \mathbf{x}_t\right) \quad p_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_{t-1} \mid \mathbf{x}_t\right)=\mathcal{N}\left(\mathbf{x}_{t-1} ; \boldsymbol{\mu}_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_t, t\right), \boldsymbol{\Sigma}_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_t, t\right)\right)\)
DDPM (2020)
DDPM 2 将 \(p_\theta\left(x_{t-1} \mid x_t\right)=\mathcal{N}\left(x_{t-1} ; \mu_\theta\left(x_t, t\right), \Sigma_\theta\left(x_t, t\right)\right)\) 中的方差设置为常数 $\beta_t$, 所以可学习的参数就只在均值中,用以下过程进行估计:
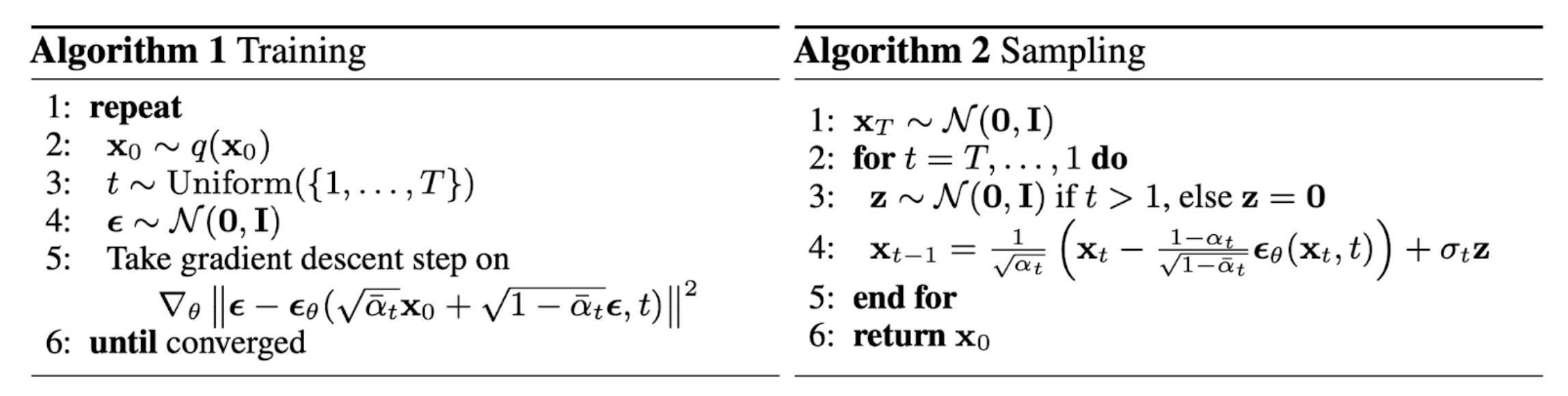
DDIM (2020)
Let \(\sigma_t^2=\eta \cdot \tilde{\beta}_t\) such that we can adjust $\eta$ as a hyperparameter to control the sampling stochasticity. The special case of $\eta=0$ makes the sampling process deterministic. Such a model is named the denoising diffusion implicit model3. DDIM has the same
LDM (2022)
Latent diffusion model 4 runs the diffusion process in the latent space instead of pixel space, making training cost lower and inference speed faster. It is motivated by the observation that most bits of an image contribute to perceptual details and the semantic and conceptual composition still remains after aggressive compression. LDM loosely decomposes the perceptual compression and semantic compression with generative modeling learning by first trimming off pixel-level redundancy with autoencoder and then manipulate/generate semantic concepts with diffusion process on learned latent.1
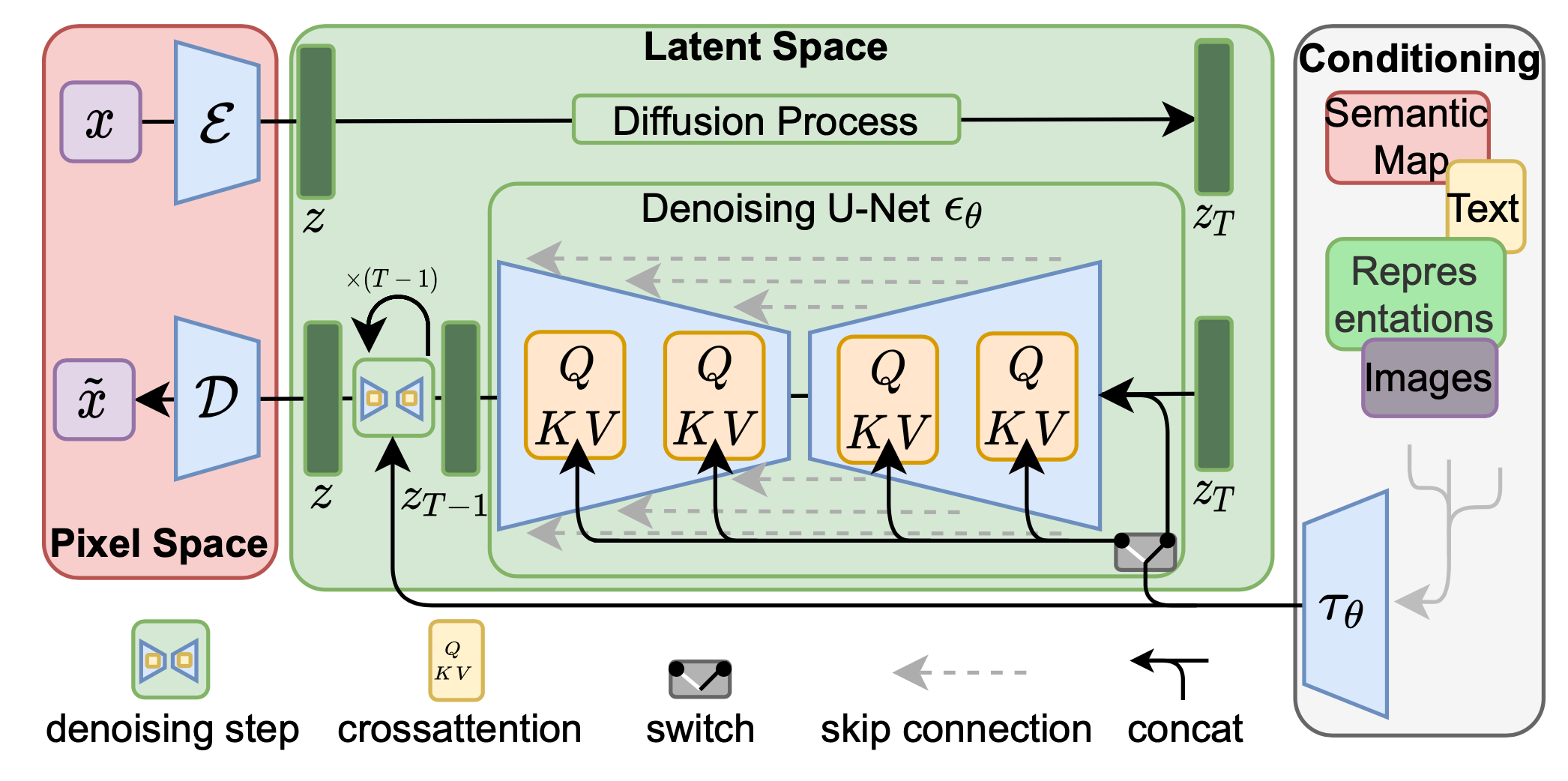
Two types of regularization:
- KL-reg: A small KL penalty towards a standard normal distribution over the learned latent, similar to VAE.
- VQ-reg: Uses a vector quantization layer within the decoder, like VQVAE but the quantization layer is absorbed by the decoder.
The diffusion and denoising processes happen on the latent vector $\mathbf{z}$. The denoising model is a time-conditioned U-Net, augmented with the cross-attention mechanism to handle flexible conditioning information for image generation (e.g. class labels, semantic maps, blurred variants of an image). The design is equivalent to fuse representation of different modality into the model with cross-attention mechanism. Each type of conditioning information is paired with a domain-specific encoder $\tau_\theta$ to project the conditioning input $y$ to an intermediate representation that can be mapped into cross-attention component, $\tau_\theta(y) \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times d_\tau}$ : \(\begin{aligned} & \operatorname{Attention}(\mathbf{Q}, \mathbf{K}, \mathbf{V})=\operatorname{softmax}\left(\frac{\mathbf{Q} \mathbf{K}^{\top}}{\sqrt{d}}\right) \cdot \mathbf{V} \\ & \text { where } \mathbf{Q}=\mathbf{W}_Q^{(i)} \cdot \varphi_i\left(\mathbf{z}_i\right), \mathbf{K}=\mathbf{W}_K^{(i)} \cdot \tau_\theta(y), \mathbf{V}=\mathbf{W}_V^{(i)} \cdot \tau_\theta(y) \\ & \text { and } \mathbf{W}_Q^{(i)} \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times d_\epsilon^i}, \mathbf{W}_K^{(i)}, \mathbf{W}_V^{(i)} \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times d_\tau}, \varphi_i\left(\mathbf{z}_i\right) \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times d_\epsilon^i}, \tau_\theta(y) \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times d_\tau} \end{aligned}\)
Conditioned Generation
目标就是利用文本(or 其他模态)提示来引导DM生成样本。
Classifier Guided Diffusion5
只要我们有了一个能分辨t时间步上噪声图像$x_t$和条件$y$的分类器f,就可以利用f的梯度引导denoising的过程。
Classifier-Free Guidance6
分类器的梯度估计根据贝叶斯公式,可以用条件生成概率和无条件生成概率表示,把这个概率代回classifier guidance的分类器梯度7
之后发现只需要一个无条件生成模型和一个条件生成模型就可以完成训练。但这两个模型可以用同一个模型表示,训练时只需要以一定概率将条件置空即可。
Reference
-
What are Diffusion Models? https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2021-07-11-diffusion-models/. ↩ ↩2
-
Ho, Jonathan, Ajay Jain, and Pieter Abbeel. “Denoising diffusion probabilistic models.” Advances in neural information processing systems 33 (2020): 6840-6851. ↩
-
Song, Jiaming, Chenlin Meng, and Stefano Ermon. “Denoising diffusion implicit models.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.02502 (2020). ↩
-
Rombach, Robin, et al. “High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2022. ↩
-
Dhariwal, Prafulla, and Alexander Nichol. “Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis.” Advances in neural information processing systems 34 (2021): 8780-8794. ↩
-
Liu, Xihui, et al. “More control for free! image synthesis with semantic diffusion guidance.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. 2023. ↩
-
通俗理解Classifier Guidance 和 Classifier-Free Guidance 的扩散模型 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/640631667 ↩