[TOC]
Abs
Challenge: Unstructured model pruning 和 highly-structured tensor core 1 hardware不适配
Observation:bottleneck of generative model inference is the several skinny matrix multiplications (decode阶段)。Decode stage would be significantly under-utilized due to low computational intensity
insight: 解决IO-bound,允许一部分冗余计算。address the significant memory bandwidth bottleneck while tolerating redundant computations that are not critical for end-to-end performance on tensor cores
Intro
这句话说挺好:There are three basic characteristics for practical model inference: accuracy, efficiency (i.e., latency and throughput), and cost (i.e., how much hardware resource it consumes).
现有的model pruning方法存在两个问题:
- difficult to support unstructured sparsity on tensor core architectures efficiently, especially since the unstructured sparse MatMul (SpMM) is hard to support on the high-performance but highly-structured tensor core architecture.
- 实现的不好。cuda上实现的特别好,tensor core上实现的不好。the state-of-the-art unstructured SpMM implementations (e.g. cuSPARSE [40], Sputnik [10]) can not even outperform the dense counterpart (cuBLAS [39]) until the model sparsity is higher than 98% and 86%, respectively.
Insight:an innovative approach to support unstructured sparsity on tensor cores by leveraging sparse memory load to improve the limited memory bandwidth while effectively tolerating redundant tensor-core computation.
Challenges:
- sparse data storage and extraction
- designing the MatMul computation pipeline
*SIMT Cores (aka. CUDA Cores) vs. Tensor Cores
GPU计算的简短历程:
- GPGPU:最早期的GPU只有渲染功能,此时要使用GPU帮助计算,需要用图形API将计算任务包装为渲染任务
- CUDA:NVIDIA开放的通用计算方式,利用GPU中大量的CUDA cores使用SIMT (Single Instruction Multiple Threads) 驱动并行计算,但是计算粒度太低,即一个周期中只完一个 FMA (Fused Multiply-Add) instruction on scalar value
- Tensor Cores:自Volta架构以来,tensor cores的引入使得一个矩阵乘能够在1个时钟周期内完成,即加速GEMM(general matrix multiplication)
对比:
- 计算速度:Tensor core快
- 计算精度:CUDA core精度高
- 通用:CUDA更通用,包括渲染、数据处理;Tensor更多用于混合精度运算
Bg
Inference Performance Hotspot of LLMs
论文说主要有4个MatMuls限制了Attention Layer的性能:
- QKV Projection
- Output Projection
- MLP1
- MLP2
其实这里还有两个MatMuls在Multi-Head Attention里,但是这两个操作不是IO-Bound的,因为
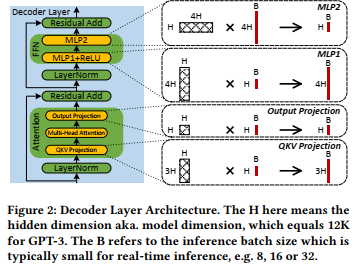
和Flash、Flat的区别: 字如其名,注意flashLLM研究对象是LLM的基本单元Transformer Block,且考虑自回归。但是Flash、Flat研究对象是Self Attention,且不考虑自回归。
Skinny Matrix Multiply
可以看到这四个MatMuls的新能受制于B的大小,这个B一般很小,因此这个矩阵是Skinny的,这个乘法近似于矩阵向量乘法。其实这个问题本质上就是Decode阶段的“IO-bound”问题。
SIMT vs. Tensor cores
SIMT cores (aka. CUDA cores) are general-purpose execution units that handle a wide range of instructions for parallel execution, while tensor cores 23are specialized units designed specially to accelerate dense MatMul computations. Tensor cores provide signi”cant acceleration for dense MatMuls, e.g. 16x higher throughput than SIMT cores in A100 GPUs with FP32 accumulation.
Conventional techniques leveraging SIMT cores for sparse MatMuls can not be directly applied to tensor cores as SIMT and tensor cores work at very different granularity. SIMT cores work on the granularity of scalar values, e.g. the FMA instruction on scalar value. The per-element granularity makes it easy to do computation skipping at the element level for SpMM. However, tensor cores work at a much more coarse-grained granularity than SIMT cores, e.g., perform a matrix multiply between two matrices with the shapes of 16 x 16 and 16 x 8 in each instruction. Thus, tensor cores do not allow skipping arbitrary element-level computations.
motivation
Unstructured Sparsity on Tensor Cores
Unstructured Pruning不需要额外constraint,而且accuracy损失相对较小。但是之前工作都是集中在SIMT上,而很少使用复杂但是高效的tensor cores。
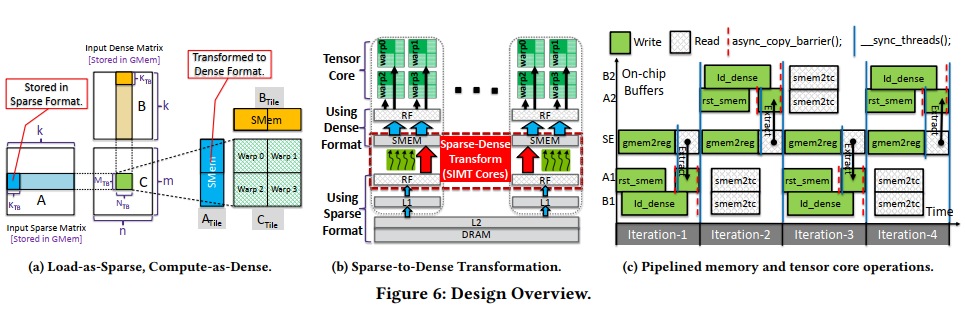
Load-as-Sparse and Compute-as-Dense
the GPU kernel loads the weight matrices from global memory in sparse format with reduced size and reconstructs the corresponding dense format in high-speed on-chip buffers for tensor core computation. The key insight is that the bottleneck for LLM inference is not at the computation side thus we can tolerate the redundant computations with tensor cores.
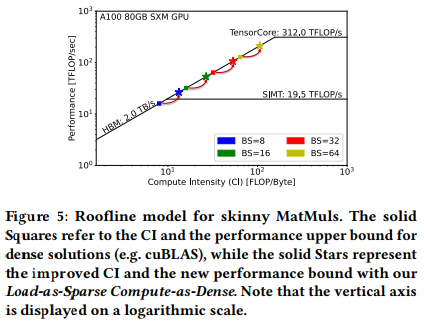
- 本质上是让Compute intensity($CI = FLOPs/Bytes $)的分母减小从而增大CI,缓解decode阶段的Memory-Bound问题。
- 有一个值得注意的问题是对于LLM的memory-bound问题是可以通过增大bs缓解的,而FLAT的问题不能
Method
The flexible SIMT cores are exploited for Sparse-to-Dense Transformation (i.e., Loadas-Sparse) while tensor cores are used for compute-intensive tensor computations (i.e., Compute-as-Dense)
主要使用了两个技术:
- intra-iteration & inter-iteration Overlapping:由于LLM推理中op是sparse与dense计算,而按照Load-as-Sparse and Compute-as-Dense思想,需要把sparse转dense,因此可以把load dense和sparse transformation执行overlap (intra-iteration overlapping)。并且自然地将computation和memory操作overlap(inter-iteration overlapping)
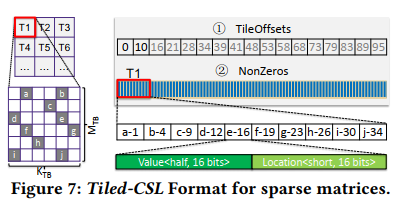
- Tiled-CSL格式:设计了对应的sparse格式和编译、内存访问优化。非零元素按 tile 组织,每个 tile 包含非零元素和对应的稀疏索引。这些数据被编码成一个小数组,所有 tile 的数组组合起来形成整体的 NonZeros Array。此外,还有一个TileOffsets数组,用来维护NonZeros数组中每个瓦片的起始偏移量。
Reference
-
Cuda Core VS Tensor Core https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/644421551 ↩
-
NVIDIA. 2022. NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU Architecture. https://www.hpctech.co.jp/catalog/gtc22-whitepaper-hopper_v1.01.pdf. ↩
-
NVIDIA. 2020. NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPU Architecture. https://images.nvidia.com/aem-dam/en-zz/Solutions/data-center/nvidia-amperearchitecture-whitepaper.pdf. ↩