[TOC]
Abs
主要关注的是inference时候的computationally expensive
以往搞sparse的有两个问题:
- 忽略LLM的in-context learning能力,要retrain一下
- 不能再hardware上实现wall-clock time speedup
介绍了一个新概念:Contextual Sparsity:small, input-dependent sets of attention heads and MLP parameters that yield approximately the same output
因此可以预测这种sparsity来实现加速,论文称 without compromising LLM’s quality or in-context learning ability.
Intro
传统的sparse方法有两个局限:
-
传统的pruning有一个问题就是说 iterative pruning and lottery ticket hypothesis (Lee et al., 2018; Frankle & Carbin, 2018) 是不适用于LLM的(似乎这个是LeCun 1984年开始做剪纸时候的一个基本假设)
-
无法保持LLM的ICL能力,sparse和硬件的不兼容
challenges:
-
existence:论文给了一个所谓theoretical understanding,但是最主要还是fig1(a)经验验证
-
prediction:contextual sparsity 分为两个部分:contextual sparsity depends not only on individual input tokens (i.e., non-contextual dynamic sparsity) but also on their interactions (contextual dynamic sparsity)
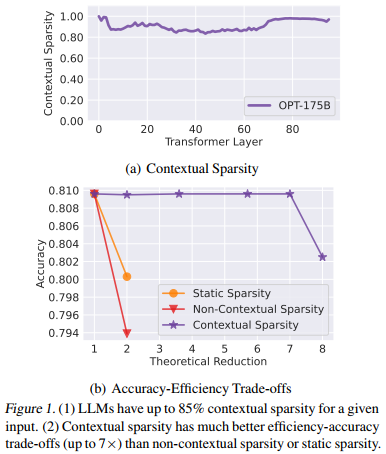
两个观察:
1)只用individual input tokens 或者 interactions 预测都不准,Only with token embeddings with sufficient contextual information can we predict sparsity accurately
2)contextual dynamic sparsity for every layer can be predicted based on the “similarity” between layer parameters (heads/MLP) and the output from the previous layer, which carries the immediate contextual mixture of token embeddings.
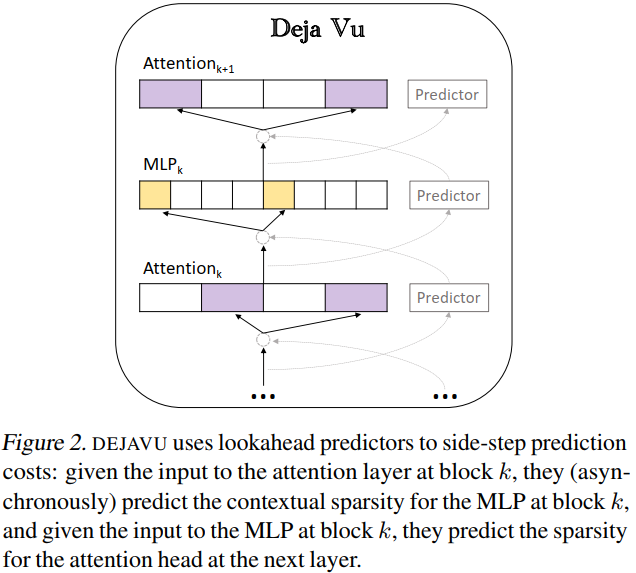
- efficiency:prediction 可以建模成一个 similarity-based problem as an NNS (Indyk & Motwani, 1998b; Zhang et al.,2018; Chen et al., 2020a).
on-the-fly = dynamic
Problem Formulation
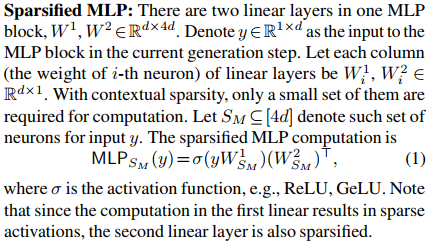
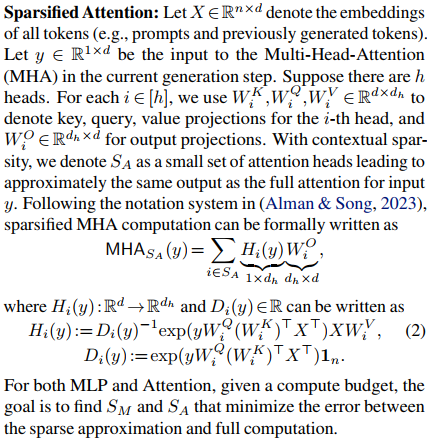
DEJAVU
Contextual Sparsity Prediction in MLP Blocks
用的是最近邻搜索的方式,因为本质上是算similarity
Contextual Sparsity Prediction in Attention Blocks
xxx
Hardware-efficient Implementation
优化了内存读写