[TOC]
Abstract
“hallucination”:the misalignment between factual visual content and corresponding textual generation
Intro
-
视觉幻觉按三元分类(ternary taxonomy): hallucination on object, attribute, and relationship
-
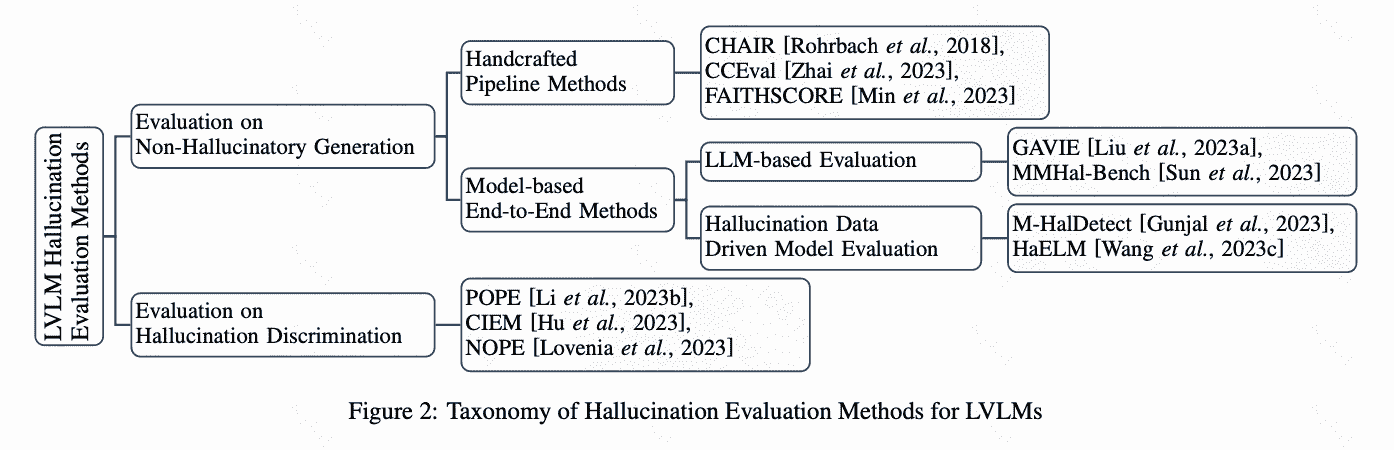
评价幻觉主要分为两个aspects:
1)non-hallucinatory generation: involves a detailed analysis of the hallucinatory elements in the model’s response and quantifying their proportion. (对generation幻觉比例进行统计分析)
2)hallucination discrimination:requires a binary judgment of whether the response comprises any hallucinatory content.(对prompt是否存在幻觉进行二分类)
- 引起幻觉的因素:
the generative nature of LLMs(架构)
biased training data(数据)
the inability of vision encoders to accurately ground images(视觉编码器)
misalignment among different modalities(对齐)
insufficient context attention(注意力缺失)
etc.
Eval Methods & Benchmarks
Causes of LVLM Hallucinations
按MLLM的全流程来看可以这样分类:
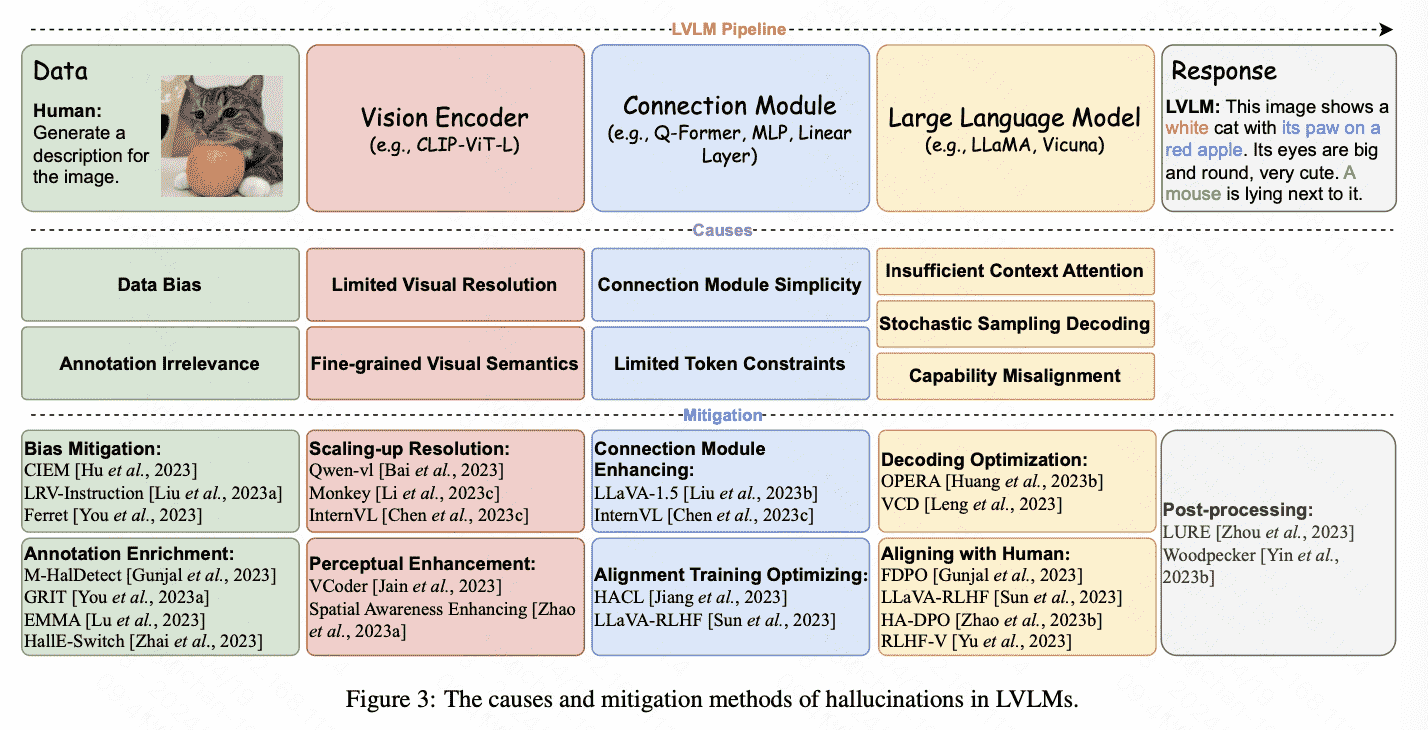
| pipeline stage | cause | description |
|---|---|---|
| Data | data bias | 主要是distribution imbalance,类别分布不均衡造成的 |
| annotation irrelevance | 大家用LLM来做数据标注,这本身不可靠 | |
| Vision Encoder | limited resolution | 分辨率不够 |
| fine-grid visual semantics | CLIP方法对比的都是图片主体,忽略了细粒度的对比学习 | |
| Modality Aligning | connection module simplicity | 线性层始终是不行的呗,表达能力不强 |
| limited token constraint | 用cross_att导致token数量受限,有loss | |
| LLM | insufficient context attention | 对img tokens对att随长度衰减(以为attention的局部性) |
| stochastic sampling decoding | 随机解码 | |
| capability misalignment | Capability misalignment in LLMs is the disparity between the model’s inherent capabili- ties that established during the pre-training phase, and the expanded requirements imposed during the instruction tuning. |
Mitigating Method
对应上面的问题解决
OPERA1
Future Work
1)Supervision Objective
2)Enriching Modalities
3)LVLMs as Agent
4)Delving into Interpretability(可解释性)
Reference
-
OPERA: Alleviating Hallucination in Multi-Modal Large Language Models via Over-Trust Penalty and Retrospection-Allocation. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2311.17911.pdf ↩